What is DTP (Dynamic Trunking Protocol)
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) is a Cisco proprietary trunking protocol, which is used to automatically negotiate trunks between Cisco switches. Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) can be used to negotiate and form trunk connection between Cisco switches dynamically.
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) can also be used for negotiating the encapsulation type of either IEEE 802.1Q or Cisco ISL (Inter-Switch Link).
Please note that Cisco ISL (Inter-Switch Link) is no more a widely accepted trunking standard. Many of the recent Cisco switches only support IEEE 802.1Q trunking standard.

Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) can operate in different trunking modes, as shown below.
| DTP Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| dynamic desirable | A switch port configured as DTP dynamic desirable mode will actively try to convert the link to a trunk link using Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP). If the port connected to other port is capable to form a trunk, a trunk link will be formed. The interface which is configured as DTP dynamic desirable mode will generate DTP messages on the interface. If the switch receive DTP messages from the other side switch, it will assume that other side port is capable for handling tagged frames and a trunk link will be formed between two switches. |
| dynamic auto | A switch port configured as DTP dynamic auto is capable to form trunk link if the other side switch interface is configured to form a trunk interface and can negotiate with trunk using DTP. A switch interface which is configured as DTP "dynamic auto" mode will not generate DTP messages on the interface. DTP "dynamic auto" interface will only listen passively for DTP messages from other side switch's interface. If the DTP dynamic auto interface receives a DTP message from the interface of the other side switch, a trunk link will be formed. |
| trunk | A switch interface which is configured as trunk mode converts the switche's interface to pure trunking mode. A trunk mode interface can also negotiate with the other side switch interface to form a trunk link between two switches. |
| nonegotiate | The nonegotiate mode disables sending DTP packets from an interface. "nonegotiate" mode is possible only when the interface switchport mode is "access" or "trunk". DTP is disabled. |
| access | A switch interface which is configured as access mode converts the switche's interface to access mode. "access" mode prevents the use of trunking and make the port as a pure access port. No frame tagging will happen in an access port. An access port belogs to a VLAN. |
Following are the different combinations of switchport modes configured in two connecting interfaces.
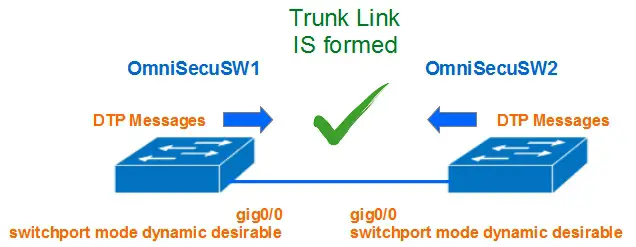
1) Both interfaces are configured with "dynamic desirable" mode
When both the two connecting interfaces are configured as DTP dynamic desirable mode, both interface will generate DTP messages. Both interface can see that the other interface is capable to form a trunk.
A trunk link will be established between two switches.
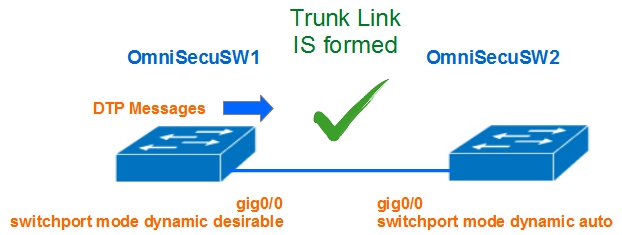
2) One interface is configured with "dynamic desirable" mode and other interface is configured with "dynamic auto" mode
A switch interface which is configured as DTP "dynamic auto" mode will not generate DTP messages on the interface. DTP "dynamic auto" interface will only listen passively for DTP messages from other side switch's interface. If the DTP dynamic auto interface receives a DTP message from the interface of the other side switch, a trunk link will be formed.
When one interface is configured as DTP "dynamic desirable" mode and other interface is configured as "dynamic auto" mode, the interface configured with "dynamic desirable" mode will generate DTP messages and try to convert the interface configured with "dynamic auto" mode to a trunk interface. Interface configured with "dynamic auto" can see that the other end interface is capable to form a trunk.
A trunk link will be established between two switches.
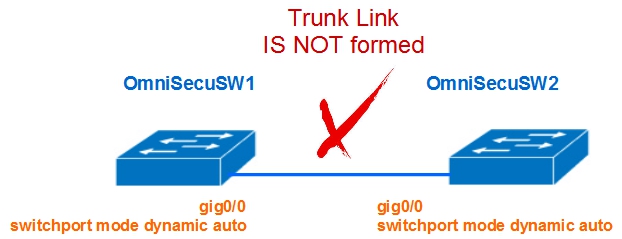
3) Both interfaces are configured with "dynamic auto" mode
When both the two connecting interfaces are configured as DTP "dynamic auto" mode, both interface will not generate DTP messages. Interfaces can not see whether the other interface is capable to form a trunk.
A trunk link will not be established between two switches.
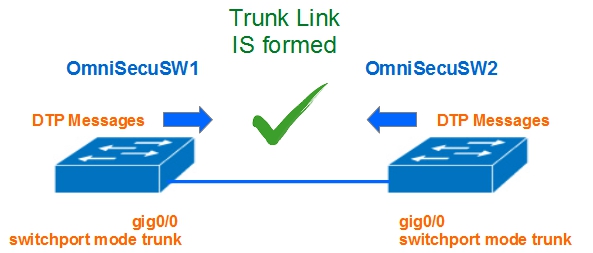
4) Both interfaces are configured with "trunk" mode
When both interfaces are configured with "trunk" mode, DTP messages are exchanged and trunk link will be established between two switches.
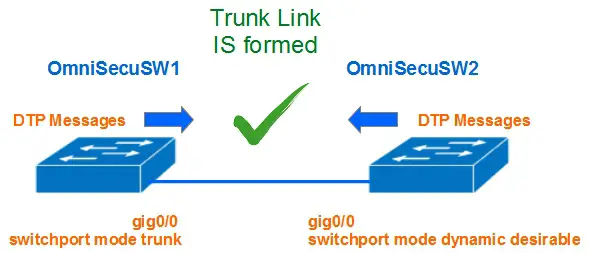
5) One interface is configured with "trunk" mode and other interface is configured with "dynamic desirable" mode
When one interface is configured with "trunk" mode and other interface is configured with "dynamic desirable" mode, DTP messages are exchanged and a trunk link is established between two switches.
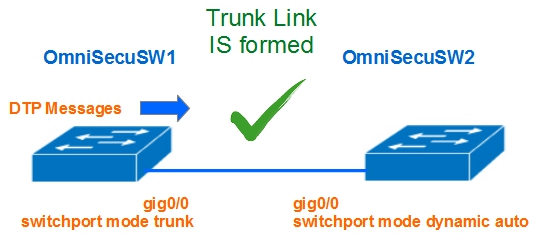
6) One interface is configured with "trunk" mode and other interface is configured with "dynamic auto" mode
When interface is configured with "trunk" mode and other interface is configured with "dynamic auto" mode, "trunk" mode interface will generate DTP messages and a trunk link is established between two switches.
Following table summarizes different combinations of switch port modes.
| Switchport Mode | dynamic desirable | dynamic auto | trunk | access |
| dynamic desirable | trunk | trunk | trunk | access |
| dynamic auto | trunk | access | trunk | access |
| trunk | trunk | trunk | trunk | access |
| access | access | access | access | access |