Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol DHCP, How DHCP work, DHCP tutorials, DHCP messages
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is used to dynamically (automatically) assign TCP/IP configuration parameters to network devices (IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS server etc). Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is described in RFC 1531. Other RFCs related with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) are RFC 1534, RFC 1541, RFC 2131, and RFC 2132. DHCP is an IETF standard based on the BOOTP protocol. A computer that gets its configuration information by using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is known as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client. DHCP clients communicate with a DHCP server to obtain IP addresses and related TCP/IP configuration information. DHCP server should be configured properly by the DHCP administrator.
Using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), DHCP Clients cab be configured with TCP/IP configuration values like IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS Server, DNS suffix etc.
How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Works?
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client TCP/IP software is not configured with a static IP address and it is configured to obtain an IP address dynamically from a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server. When a DHCP client device boots up, it not capable send and receive network traffic, because TCP/IP is not configured. But it can participate in broadcast traffic. DHCP Clients and DHCP Servers uses broadcast messages to communicate with each other. The scope of a broadcast message is only within the local broadcast domain. Broadcast messages will never cross the router to reach another network, because Routers drop Limited Broadcast IP Address.
Two important IPv4 addresses used in DHCPv4 messages are 0.0.0.0 and 255.255.255.255. IPv4 address 0.0.0.0 is used by an IPv4 device, when it has not yet been assigned an IPv4 address. When a DHCP client boots up, it doesnt have a valid IPv4 Address.
IPv4 address 255.255.255.255 is also known as Limited Broadcast IP Address. An IPv4 datagram with 255.255.255.255 as destination IPv4 address is broadcasted in the LAN.
DHCPDISCOVER and DHCPREQUEST messages are sent from DHCP Client to DHCP Server. DHCPOFFER and DHCPACK messages are sent from DHCP Server to DHCP Client.
The process of leasing TCP/IP configuration from the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server involves four steps as listed below.
1. DHCPDISCOVER: The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client broadcasts a DHCP discover message on the network containing its MAC address destined for UDP port number 68 (used by BOOTP and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) servers). This first datagram is known as a DHCPDISCOVER message, which is a request to any DHCP Server that receives the datagram for configuration information. As the name implies, the purpose of DHCPDISCOVER mesage is to discover a DHCP server.
As you can see from the screenshot copied below, the destination MAC Address of a DHCPDISCOVER message is ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, which is the Broadcast MAC Address. An Ethernet Frame with Broadcast MAC Address as the destination MAC Address is flooded to every port of the connected LAN Switch. DHCPDISCOVER message is delivered to every connected computer in the Broadcast Domain.
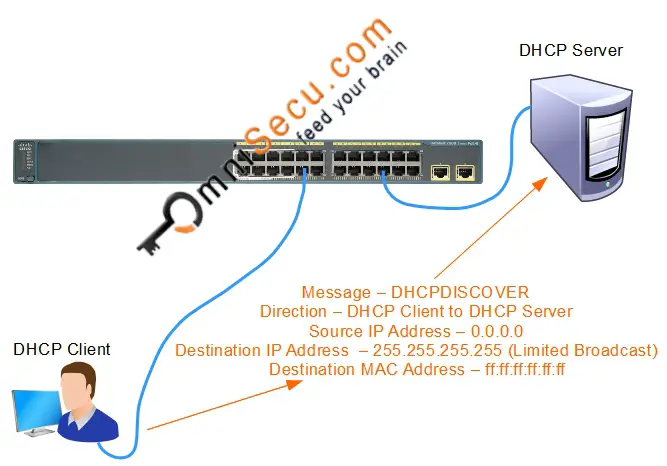
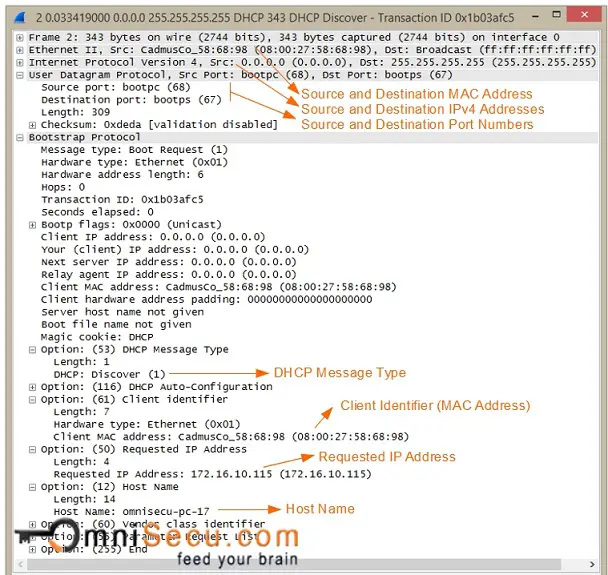
Key values to remember for a DHCPDISCOVER message are tabulated below.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Message Direction | DHCP Client to DHCP Server |
| Source MAC Address | Interface MAC Address of DHCP Client |
| Destination MAC Address | ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (Broadcast MAC Address) |
| Source IPv4 Address | 0.0.0.0 |
| Destination IPv4 Address | 255.255.255.255 (Limited Broadcast) |
| Source Port Number | UDP 68 |
| Destination Port Number | UDP 67 |
2. DHCPOFFER: DHCPDISCOVER Message was delivered to every connected computers in the Broadcast Domain. Every DHCP Server in the Broadcast Domain which received the DHCPDISCOVER message responds with a DHCPOFFER message. Other computers simply drop the DHCPDISCOVER Message.
DHCPOFFER Message contains the offered TCP/IP Configuration values like IPv4 address and subnet mask. If the DHCP client device received multiple DHCPOFFER, the DHCP client accepts the first DHCPOFFER Message that arrives.
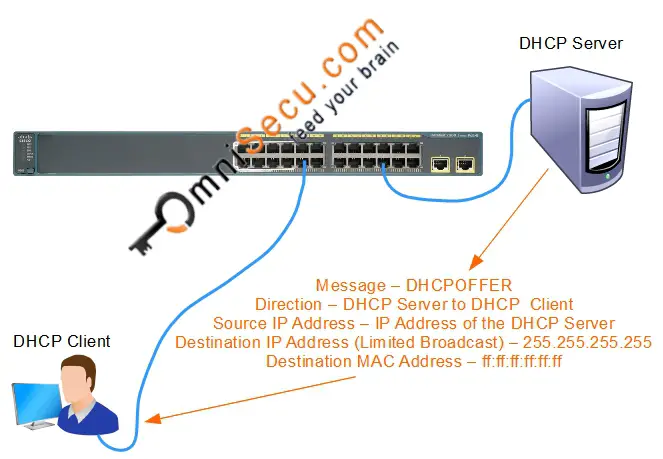
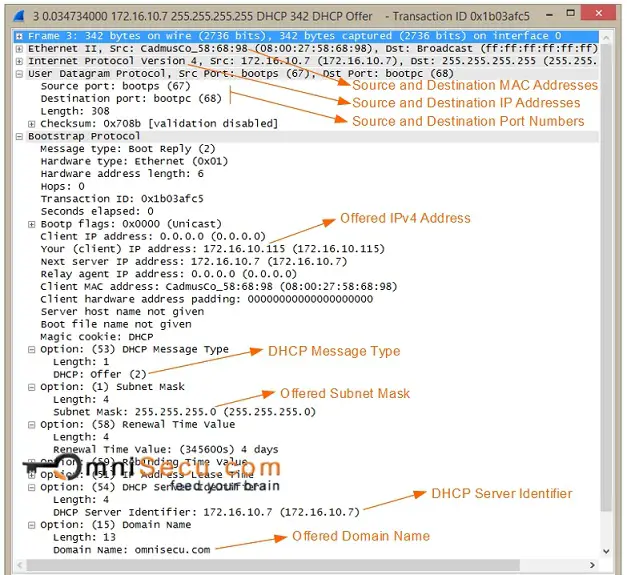
Key values to remember for a DHCPOFFER message are tabulated below.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Message Direction | DHCP Server to DHCP Client |
| Source MAC Address | Interface MAC Address of DHCP Server |
| Destination MAC Address | ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (Broadcast MAC Address) |
| Source IPv4 Address | Interface IPv4 Address of DHCP Server |
| Destination IPv4 Address | 255.255.255.255 (Limited Broadcast) |
| Source Port Number | UDP 67 |
| Destination Port Number | UDP 68 |
3. DHCPREQUEST: The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) client accepts an offer and broadcasts a DHCPREQUEST datagram. The DHCPREQUEST datagram contains the IP address of the server that issued the offer and the physical address (MAC Address) of the DHCP client. DHCPREQUEST message requests the selected DHCP server to assign the DHCP client an IP address and other TCP/IP configuration values. DHCPREQUEST message also notifies all other DHCP servers that their offers were not accepted by the DHCP client.
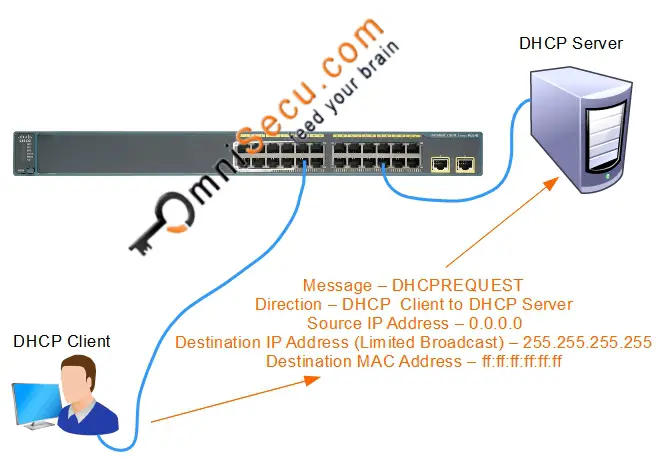
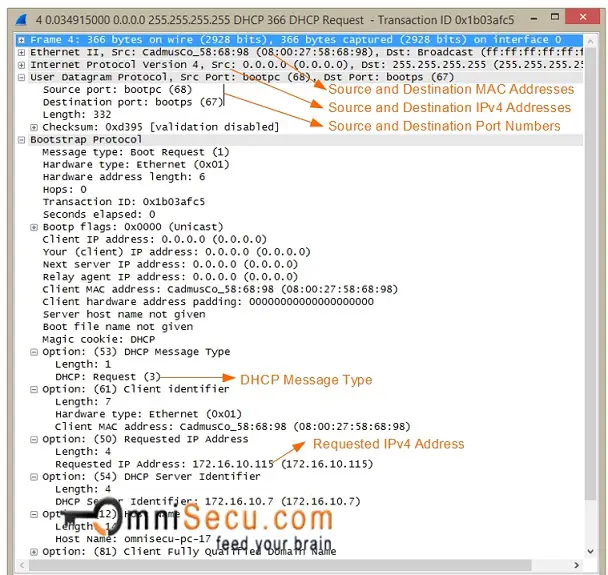
Key values to remember for a DHCPREQUEST message are tabulated below.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Message Direction | DHCP Client to DHCP Server |
| Source MAC Address | Interface MAC Address of DHCP Client |
| Destination MAC Address | ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (Broadcast MAC Address) |
| Source IPv4 Address | 0.0.0.0 |
| Destination IPv4 Address | 255.255.255.255 (Limited Broadcast) |
| Source Port Number | UDP 68 |
| Destination Port Number | UDP 67 |
4. DHCPACK: When the DHCP server from which the offer was selected receives the DHCPREQUEST datagram, it constructs a DHCPACK datagram. This datagram is known as a DHCPACK (DHCP ACKNOWLEDGEMENT). The DHCPACK includes an IP address and subnet mask for the DHCP client. It may include other TCP/IP configuration information like IP address of the default gateway, IP addresses of DNS servers, IP addresses of WINS servers etc.
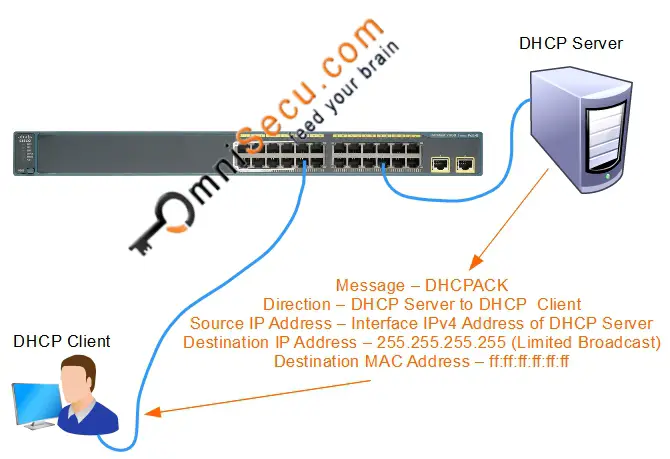
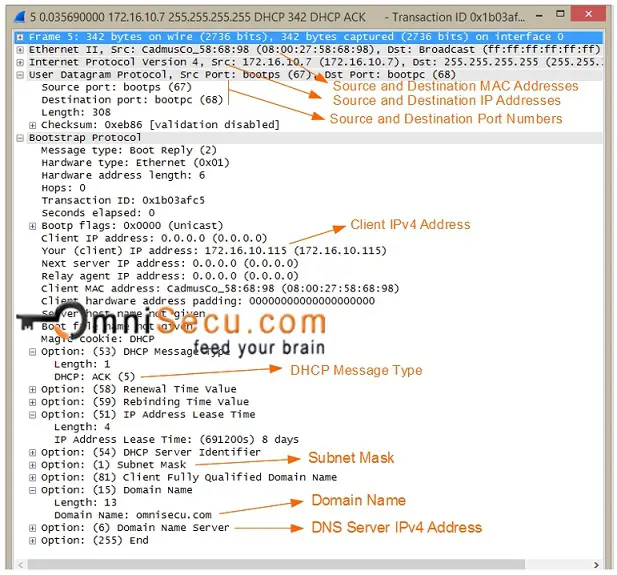
Key values to remember for a DHCPACK message are tabulated below.
| Description | Value |
|---|---|
| Message Direction | DHCP Server to DHCP Client |
| Source MAC Address | Interface MAC Address of DHCP Server |
| Destination MAC Address | ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff (Broadcast MAC Address) |
| Source IPv4 Address | Interface IPv4 Address of DHCP Server |
| Destination IPv4 Address | 255.255.255.255 (Limited Broadcast) |
| Source Port Number | UDP 67 |
| Destination Port Number | UDP 68 |
Once the DHCPACK message is received from the DHCP Server, DHCP Client can start using that IPv4 Addrees.
You have learned Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and how Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) works. To continue to the next part of Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), click "Next".