How fiber optics works
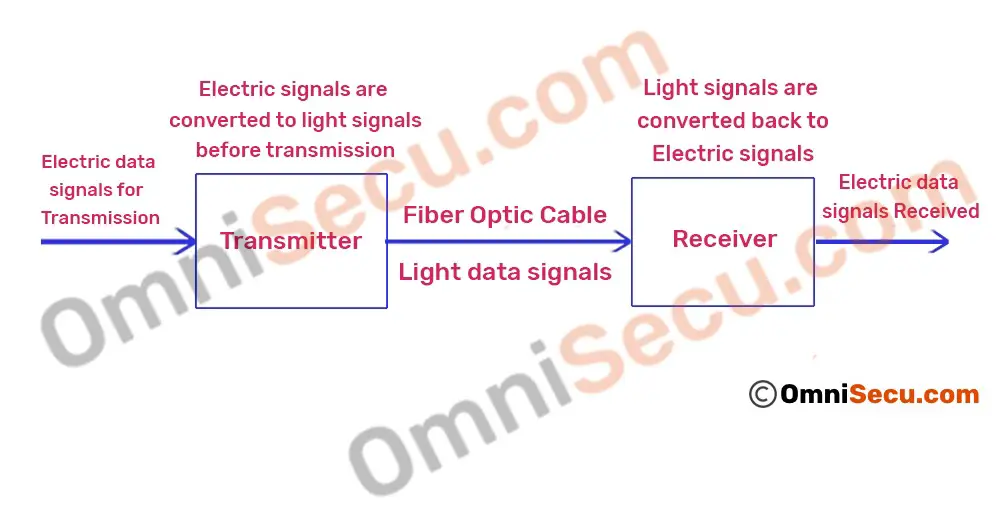
Fiber optic system can transfer data using pulses of light instead of electric signals. Electrical signals are converted to light signals and sent and received by transceivers on both sides of the fiber optic cable.
A fiber optic system contains following components.
Transmitter - Generates light signals from electrical signals received from electrical circuits. Encodes and forwards the light signals to the receiver at other side of the cable.
Fiber optic cables - Carry the light signals from a place to another place over a distance.
Optical regenerator (optional) - Used for long distance signal transfer to increase the quality of the light signal.
Receiver - Receives the light signals sent from one side, decodes it and generates electrical signals from the light signals. Electrical signals are then passed to electrical circuits.