How to create and configure Standard Named Access Control Lists (ACLs)
Before continuing, refer Introduction to Access Control Lists lesson , if you are not familiar with Access Contol Lists.
Refer Standard Access Control Lists lesson if you are not familiar with Standard Access Control List configuration IOS commands.
Refer Named Access Control Lists if you are not familiar with Named Access Control Lists configuration IOS commands.
The basic IOS command to create a Named Access Control List (ACL) is shown below, which is similar to creating a Numbered Access Control List (ACL).
Router(config)# ip access-list standard|extended ACL_name
The standard and extended keywords specify whether it is a Standard Access Control List (ACL) or an Extended Access Control List (ACL).
Standard Named Access Control Lists (ACLs) - Lab Practice
The following diagram shows our Standard Named Access Control Lists lab setup. We have three routers, three switches, six workstations and three servers connected as below. The host names, IP addresses and the interfaces of the routers are shown in diagram. The IP addresses of the workstations and the servers are also shown in the diagram.
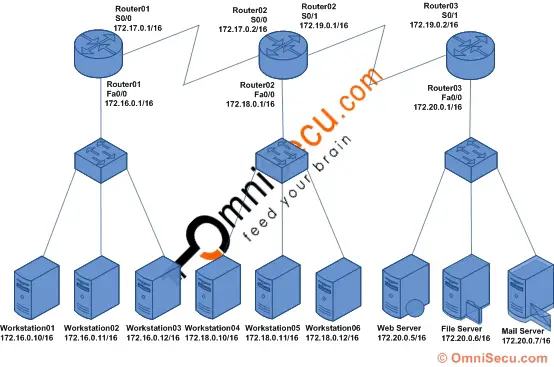
The purpose of this lab is to deny network 172.16.0.0/16 from accessing the 172.20.0.0/16 network, using Standard Named Access Control List (ACL). Connect computers, switches and routers as shown in the figure. Configure the IP address and default gateway TCP/IP settings in all computers and servers. Configure the hostname, IP address and routing on three routers. Click the following link to learn more about configuring hostnames, IP addresses and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) in routers.
Click the following link to know where to place a Standard Access Control List (ACL). In this lab, the router near to the destination network is Router03, and we have to configure Standard Named Access Control List (ACL) in Router03.
How to create Standard Named Access Control List (ACL) using "access-list" IOS command
Following IOS commands shows how to create a Standard Named Access Control List (ACL).
Router03>enable Router03#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router03(config)#ip access-list standard BLOCK_NETWORK1 Router03(config-std-nacl)#deny 172.16.0.0 0.0.255.255 Router03(config-std-nacl)#permit any Router03(config-std-nacl)#exit Router03(config)#exit %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Router03#
Remember, there is an implicit "deny any" at the end of every Access Control Lists (ACLs). If there is no "permit any" statement at the end, above Standard Named Access Control List (ACL) may filter out all traffic to the destination network. The "permit any" permits any other traffic, if there is no matching deny in previous statements. Above Standard Named Access Control List (ACL) effectively allow all the traffic to the destination network except 172.16.0.0/16 network.
If you want to remove the Access Control List (ACL), use the "no" form of the command. You cannot delete a specific entry in an Access Control List (ACL). You can only delete the entire Access Control List (ACL), as shown below.
Router03(config)#no access-list BLOCK_NETWORK1
How to configure Standard Named Access Control Lists (ACL) to an interface using "access-group" command
The Standard Named Access Control List (ACL) created above can be applied using the IOS command shown below.
Router(config)# interface interface_no
Router(config-if)# ip access-group ACL_name in|out
The "in/out" keyword of the command is used to specify the direction in which the traffic is filtered.
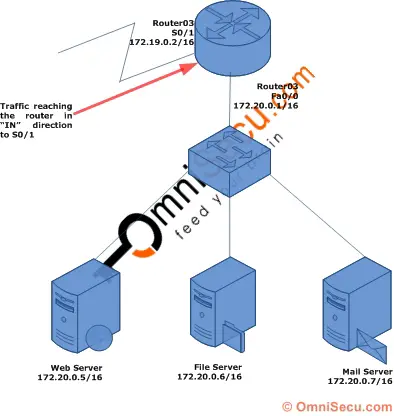
The "in" keyword is used to specify that the traffic should be filtered when it arrive the router via an interface. Following diagram explains the "in" keyword. Here the traffic will be filtered as it arrives the router.
The "out" keyword is used to specify that the traffic should be filtered as it leaves the router via an interface. Following diagram explains the "out" keyword. Here the traffic will be filtered as it leaves the router.
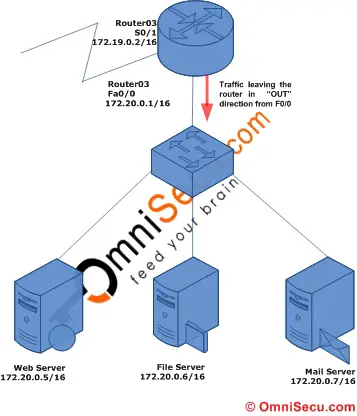
The Standard Access Control Lists must be applied close to the destination network. Here the interface close to the destination is fa0/0 in Router03. Following IOS commands apply the Standard Named Access Control List (Access Control List Name - BLOCK_NETWORK1) to the interface fa0/0 (Router03) in "out" direction.
Router03>enable Router03#configure terminal Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. Router03(config)#interface fa0/0 Router03(config-if)#ip access-group BLOCK_NETWORK1 out Router03(config-if)#exit Router03(config)#exit Router03# %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console Router03#
If you want to remove the Access Control List (ACL) from the above interface, use the "no" form of the command as shown below.
Router01(config-if)#no ip access-group BLOCK_NETWORK1 out