What is GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation)
Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) is an IP encapsulation protocol which is used to transport IP packets over a network. Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) was initially developed by Cisco, but later become industry standard (RFC 1701, RFC 2784, RFC 2890).
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) can tunnel any Layer 3 protocol including IP. In GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) an IP datagram is tunnelled (encapsulated) within another IP datagram.
One great advantage of GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) is that it allows routing of IP packets between private IPv4 networks which are separated over public IPv4 internet. GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) also supports encapsulating IPv4 broadcast and multicast traffic.
Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) tunnels are not secure because Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) does not encrypt its Data payload. In real-time, Generic routing encapsulation (GRE) used together with other secure tunnelling protocols like IPSec to provide network security.
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) Header
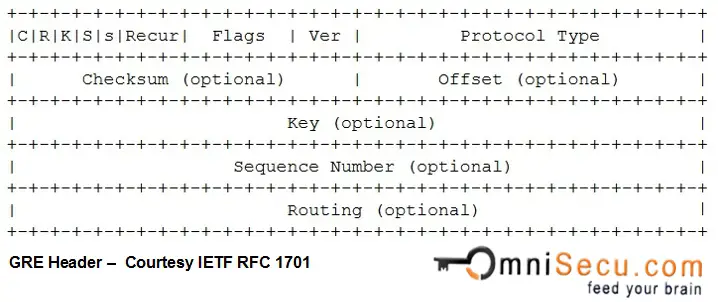
Following are the fields of Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) Header.
Flag C (Checksum Present) : Used to indicate that the Checksum field is present and contains valid information, when set to 1.
Flag R (Routing Present) : Used to indicate that the Routing fields are present and contain valid information, when set to 1.
Flag K (Key Present) : Used to indicate that the Key field is present in the GRE header, when set to 1.
Flag S (Sequence Number Present) : Used to indicate that the Sequence Number field is present, when set to 1.
Flag s (Strict Source Route) : Set to 1 the routing information consists of Strict Source Routes
Recursion Control and Version Number are normally set to 0
Protocol Type : Protocol Type field is used to mention the protocol payload of the GRE packet. For IP, this field is set to 0x800
Checksum : Checksum field value is used to check the integrity of the GRE header and the payload.
Key : Key field value is used to authenticate the GRE packet's encapsulator.
Sequence Number : Sequence Number filed value is used to track the sequence of GRE packets
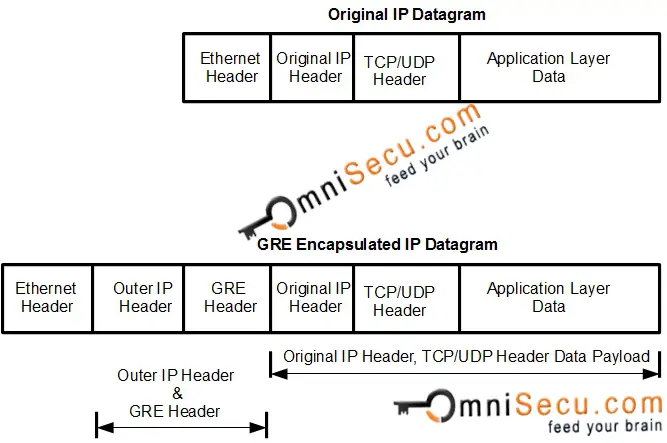
Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) Encapsulation
Following image shows the difference between original IP Datagram and Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) encapsulated IP Datagram.
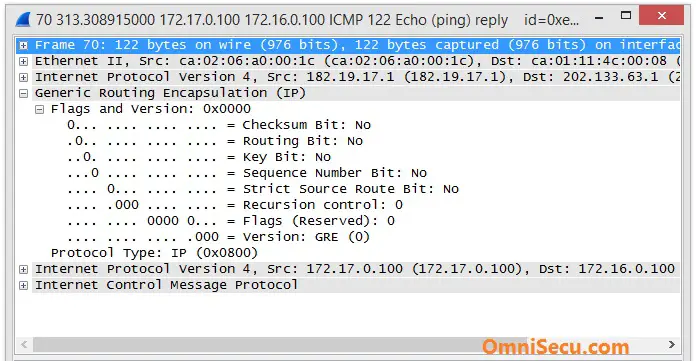
Following Wireshark capture image shows GRE Encapsulation and GRE Header fields