IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) Port Based Authentication, Supplicant, Authenticator and Authentication Server
In a large network environment consisting of large number of computers spanned over multiple buildings (For example, a university campus) it is difficult to monitor all the network end points. A network attacker can attach his laptop loaded with all different hacking tools to an enabled network port located at a corner of a building and start attacking the network.
IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) Port-Based Authentication can be used to prevent unauthorized devices from gaining access to the network. IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) Port-Based Authentication can allow network access for a device attached to a network port if the authentication process succeeded and prevent access to that port if the authentication process failed. IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) standards can provide authentication and authorization services at network port level. Main components of IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) Port-Based Authentication are listed below.
Supplicant, Authenticator and Authentication Server
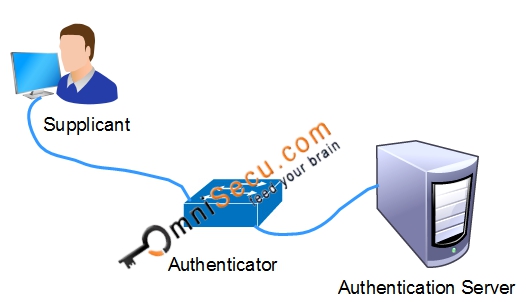
1) Supplicant: Supplicant is a network device which collects authentication credentials from end user and forwards those credentials for authentication process. Example: A software application running on a laptop attached to a network port or an Operating system related processe running on that laptop.
2) Authenticator: Authenticator is a network access device which collects the authentication credentials from the Supplicant and relay those credentials to the Authentication Server for verification. (Switch or wireless AP).
3) Authentication Server: Authentication Server is a network server that validates the credentials sent by the supplicant based on the information stored in its database and determines whether to allow network access or prevent network access to the Supplicant. Authentication Server can be any RADIUS Server.
Example: Cisco Secure ACS (Access Control Server) or Cisco ISE (Identity Services Engine).
IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) Authentication Protocols - EAPoL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) and RADIUS
The protocol used for communication between Supplicant and Authenticator is EAPoL. The protocol used for communication between Authenticator and Authentication Server is RADIUS.
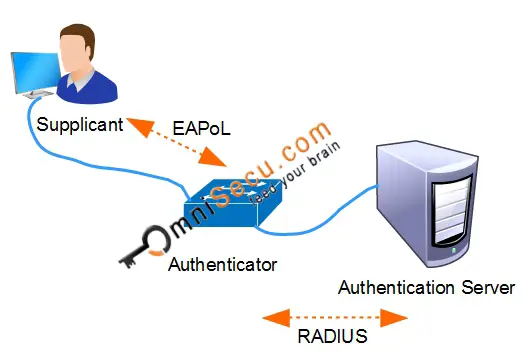
1) Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP): In an wired Ethernet network, IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) uses the Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN (EAPoL) to exchange messages during the authentication process. EAPoL (Extensible Authentication Protocol over LAN) is used to transport EAP packets between Supplicant and an Authenticator over Local Area Network (LAN). There are different Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Authentication Methods are available. Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Authentication Methods are used in the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) Authentication process. Common EAP Authentication methods used in IEEE 802.1X (dot1x) are EAP-TLS (EAP-Transport Layer Security) and PEAP-MSCHAPv2 (Protected EAP-Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version
2) RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service): The protocol used for communication between Authenticator and Authentication Server is RADIUS. RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service) is all-vendor supported AAA protocol. RADIUS was first developed by Livingston Enterprises Inc in 1991, which later merged with Alcatel Lucent. RADIUS later became an Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) standard. Some RADIUS server implementations use UDP port 1812 for RADIUS authentication and UDP port 1813 for RADIUS accounting. Some other implementations use UDP port 1645 for RADIUS authentication messages and UDP port 1646 for RADIUS accounting
Click he following link to understand how IEEE 802.1X Port Based Authentication works