IPv6 Loopback Address and IPv6 Unspecified address
The loopback address (both in IPv4 and IPv6) is an address which represents the same interface of a computer. Whenever we communicate to a loopback address (both in IPv4 and IPv6) the TCP/IP protocol stack will loop the packets back to the same interface, without even leaving the interface. The loopback addresses are typically used by programmers for development and testing of network applications without even having network configurations.
In IPv4, we have an entire network (127.0.0.0/8) reserved as loopback addresses. But almost all leading operating systems use the name "localhost" to represent an IPv4 loopback address 127.0.0.1. Rest of the addresses in 127.0.0.0/8 loop-back network are not widely used.
In IPv6, the IPv6 address reserved for loopback use is 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0001/128. This loopback address is so lengthy and can be further simplified as ::1/128. Click the below links to learn more about how to simplify and shorten an IPv6 address.
Unspecified address in IPv6 is the IPv6 address with all binary bits set to "0". In IPv4, the IPv4 address used as unspecified address is 0.0.0.0/0. Unspecified address is used by an Operating System, before an IPv4 address or IPv6 address is configured on it.
Following image shows the screen-shot of an IPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message (NS message) , where IPv6 unspecified address is used as the source IPv6 address.
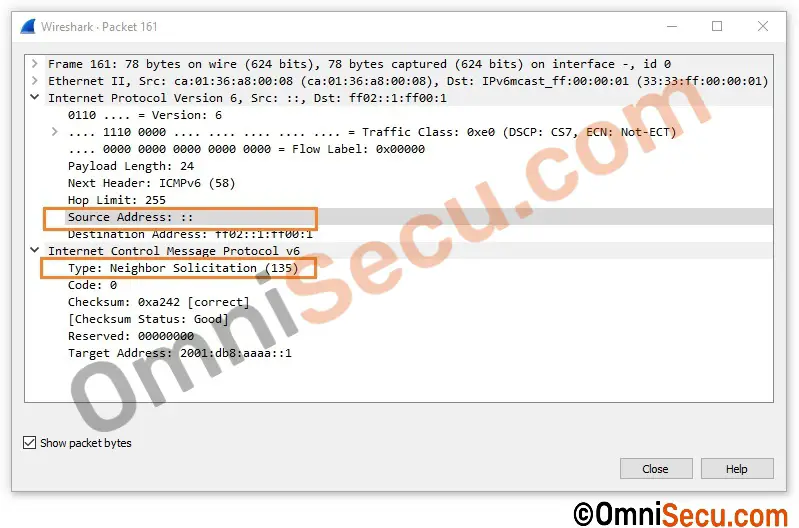
IPv4 and IPv6 routers will not forward packets with the unspecified address.
In IPv6, the unspecified IPv6 address is 0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/0. This unspecified address is so lengthy and can be further simplified as ::/0. Click the below links to learn more about how to simplify and shorten an IPv6 address. Following table shows IPv4 and IPv6 loopback and unspecified address
| Type of address | IPv4 | IPv6 |
| Loopback address | 127.0.0.1/8 | ::1/128 |
| Unspecified address | 0.0.0.0/0 | ::/0 |
Written by Jajish Thomas.
Last updated on 19th May, 2024.