Network Infrastructure devices - What is a Firewall
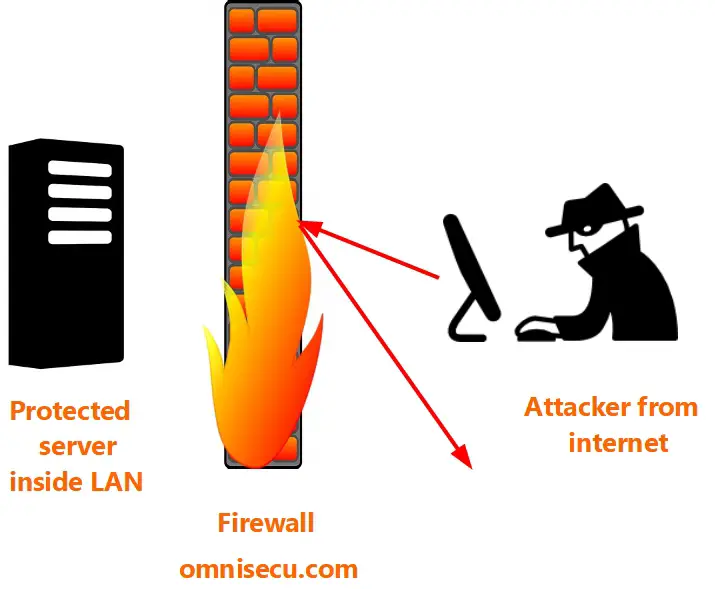
Firewall is a physical wall barricade, that can stop spreading fire in case of a fire accident. Similar to a physical wall barricade which can stop the fire from spreading, network firewalls prevent unauthorized access to or from a private network. Firewalls can enhance the security of computers in a LAN.
Firewalls are used to protect a network's data and resources from outside access and threats. A Firewall is used as a barrier between an internal network of an organization and another network (may be public internet or another network of the same organization).
Since the primary function of a Firewall is to protect a network's data and resources from outside threats, they are usually placed at the end point of a network.
A firewall can be a dedicated Hardware device, or software running in a computer. Some firewalls have custom built operating system, over which the firewall application is running. There are different types of Firewalls available. Based on their architecture and nature of operation, firewalls are divided into different categories. Some examples are; Packet filtering Firewall, Stateful inspection Firewall, Proxy Firewalls (Application level gateways/cloud Firewalls), Software Firewalls (Personal Firewall), Hardware Firewalls etc. We will learn more about different types of Firewalls in a future tutorial lesson.
Firewalls can be configured with "rules". Firewall rules can be used to allow/deny network traffic from/to the network. These rules can be based on Source/Destination network, Source/Destination IP Address, Source/Destination TCP/UDP port numbers, Protocols, Applications etc.
Following image shows a Cisco ASA 5516-X with FirePOWER Services firewall device. For more details and technical specifications, please visit official Cisco product page for Cisco ASA 5516-X Firewall with FirePOWER Services.
