What is a Designated Port
There can be only one Root Port (marked as RP) on a Switch, but a Switch can have multiple Designated ports (marked as DP). The Designated Port is the port that has the lowest Path Cost on a particular Local Area Network (LAN) segment. Each segment has a single port that is used to reach the Root Bridge (Root Switch) called Designated Port. A Root Port can never be a Designated port.
A Root Port is the port on the Switch with the least cost from the "Switch" to the Root Bridge. A Designated Port is the port on a "Local Area Network (LAN) segment" with the least cost to the root bridge. The other end of a Designated Port is called as Non Designated Port (marked as NDP), if it is NOT a Root Port. Non Designated Port will be always in Blocking State, to avoid Layer 2 Switching loops.
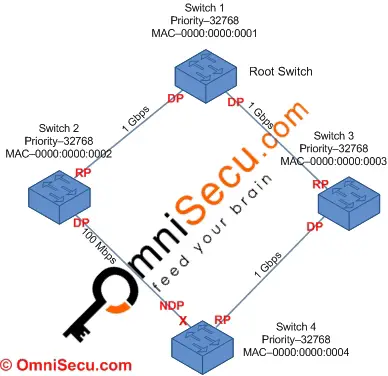
Remember, a Root Port can never be a Designated Port and also there cannot be any Root Port on a Root Bridge (Root Switch). All the ports on a Root Bridge (Root Switch) are Designated Ports.