What is Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Backbone Fast
UplinkFast, Backbone Fast and Portfast are Cisco’s proprietary extensions to the Classic Spanning Tree Protocol (STP 802.1 D) algorithm. The purpose UplinkFast, Backbone Fast and Portfast are to reduce the time it takes for classic Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to converge after a link failure.
The BackboneFast extension can dramatically decrease the convergence time of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in the event of an Indirect link (a link in any other switch, which is not connected directly) failure, anywhere in the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Topology.
Consider the following topology.
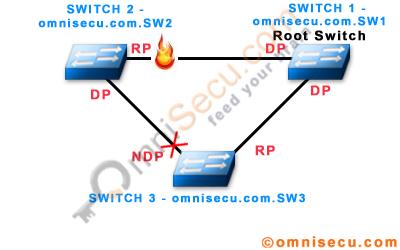
The link between Switch omnisecu.com.SW2 and omnisecu.com.SW1 (Root Switch (Root Bridge)) has failed. The link between Switch omnisecu.com.SW2 and omnisecu.com.SW1 is not a direct link for Switch omnisecu.com.SW3.
The switch omnisecu.com.SW2 detect the link failure and will immediately invalidate the best BPDU stored for its port connecting to omnisecu.com.SW1 (Root Switch (Root Bridge)). Switch omnisecu.com.SW2 will think itself as the Root Switch (Root Bridge) of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), since no other ports is receiving BPDUs from Root Switch (Root Bridge).
Now omnisecu.com.SW2 starts sending inferior BPDUs to omnisecu.com.SW3. A BPDU is considered inferior, if Root Switch (Root Bridge) information contained in it is worst compared to the information from original Root Switch (Root Bridge), or the BPDU has longer distance to reach the current Root Switch (Root Bridge). Switches can identify inferior BPDUs from higher Root Switch ID included in the inferior BPDU (a Switch with higher Switch ID cannot become the Root Switch (Root Bridge)).
For Switch omnisecu.com.SW3, the BPDU sent from omnisecu.com.SW2 is inferior, because it is still receiving better BPDUs from the current Root Switch (Root Bridge), omnisecu.com.SW1 .
If the network is running classic Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), the Switches will behave as below.
When omnisecu.com.SW3 start receiving inferior BPDUs at its interface from Switch omnisecu.com.SW2, omnisecu.com.SW3 would ignore the inferior information until the BPDU stored with the blocked port expires (max age timer in seconds).
When max age timer expires, and the Switch omnisecu.com.SW3 is still receiving inferior BPDUs from omnisecu.com.SW2, omnisecu.com.SW3 will start responding to the inferior BPDUs. The port in omnisecu.com.SW3, which received the inferior BPDUs from omnisecu.com.SW2, will move to Listening State, and omnisecu.com.SW3 will start relaying the omnisecu.com.SW1 (Root Switch (Root Bridge) BPDUs to omnisecu.com.SW2 (since the BPDUs from omnisecu.com.SW1 are superior compared to the BPDUs from omnisecu.com.SW2).
omnisecu.com.SW2 now start getting the original BPDUs from the Root Switch (Root Bridge) and move its port through Listening State and Learning State and finally Forwarding State. Both omnisecu.com.SW3 and omnisecu.com.SW2 will move their ports into forwarding states re-establishing the lost connectivity.
Therefore the time required to re-establish an indirect link failure is (max age timer + (forward delay timer + forward delay timer) which is too high for current network applications.
If Backbone Fast is enabled in the network, Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) behaves as below.
When omnisecu.com.SW3 receives an inferior BPDU from omnisecu.com.SW2, it will send a Root Link Query (RLQ) PDU on all non-designated ports (except the port where it received the inferior BPDU) to hear that the Root Switch (Root Bridge) is still available.
The port on which omnisecu.com.SW3 received the inferior BPDU from omnisecu.com.SW2 is also excluded because that path is already failed.
When a Root Link Query (RLQ) response is received on a port, if the answer is negative, the port lost connection to the root and you can age out its BPDU. If all other non-designated ports received a negative answer, Switch omnisecu.com.SW3 has lost connection to Root Switch (Root Bridge) and can start the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) calculation from beginning.
If omnisecu.com.SW3 receives any positive response, it will assume the current Root Switch (Root Bridge) is still reachable. In our case, omnisecu.com.SW3 will receive a positive response from omnisecu.com.SW1 (Root Switch (Root Bridge)), and start relaying omnisecu.com.SW1 (Root Switch (Root Bridge)), BPDUs to omnisecu.com.SW2.
Backbone Fast is pro-active (using Root Link Query (RLQ)) and when Backbone fast is implemented, it can minimize the max age timer interval. By enabling Backbone fast the max age timer can be skipped and the delay is minimized from 50 seconds to 30 seconds.