Spanning Tree Port Priority and Port ID Values
Each port of a Switch has a Spanning Tree Port Priority value associated with it, which is equal to 128 by default.
Spanning Tree Port ID is formed by adding the 4-bit port priority value (the default value of 128) to 12-bit interface identifier (total 16 bits).
Normally, a Port ID is denoted in Hexadecimals similar as 0x8015, which is equivalant to 128.21 in decimals, where the first part is the default Port Priority number and second part is the switch interface identifier.
We can view the spanning-tree command by using show command "show spanning-tree".
omnisecu.com.SW1#show spanning-tree
VLAN0001
Spanning tree enabled protocol ieee
Root ID Priority 32769
Address 0001.42AD.E8B3
This bridge is the root
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1)
Address 0001.42AD.E8B3
Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec
Aging Time 20
Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type
---------------- ---- --- --------- -------- --------------------------------
Fa0/24 Desg FWD 19 128.24 P2p
Gi1/1 Desg FWD 4 128.25 P2p
Gi1/2 Desg FWD 4 128.26 P2p
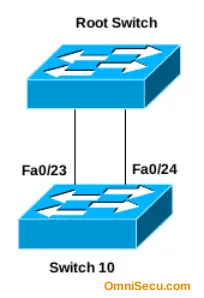
In above topology, the first two conditions to select the Root Switch will become a tie (both path has same Path Cost and same neighbour Switch ID), if the bandwidth of the two links are equal.
Here, the Port Priority number will be used as the tie-breaker. The interface on Switch 10, which receives the lowest Port Priority number from the connected switch (in this case the Root Switch), will become the Root Port, and other port will be in blocking.