IGMPv1 - Internet Group Management Protocol Version 1
As discussed in previous lesson, Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP), IGMPv1 was defined in RFC 1112. Two types of IGMPv1 messages are Membership Query (MQ) messages and Membership Report (MR) messages. Membership Query (MQ) messages are sent from Querier (local multicast router) to hosts in its connected subnet. Membership Report (MR) messages are sent from hosts to local multicast routers.
Please visit below links and learn the concepts of IPv4 multicast before proceeding further.
- Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
- Broadcast domain
- Broadcast MAC Address - ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- IPv4 multicast MAC Addresses
- IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
- IPv4 addresses
- Class D multicast IP addresses
- IPv4 link-local multicast addresses
- IPv4 Internetwork control block multicast addresses
- IPv4 Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) address reservation
- IPv4 GLOP multicast addresses
- Administratively scoped multicast address block or Limited scope addresses
- Multicast IPv4 address to MAC address mapping
- TCP/IP Encapsulation and Decapsulation
- What is multicast
- What is multicast group
- Advantages and disadvantages of multicast
- Comparison of multicast with unicast and broadcast
- Advantages and disadvantages of multicast
- How IPv4 multicast works on LAN
- IGMP, What is IGMP, How IGMP works
- IGMP message types
- IGMP DR and Querier
IGMPv1 message format
Below image shows the original format of IGMPv1 message.
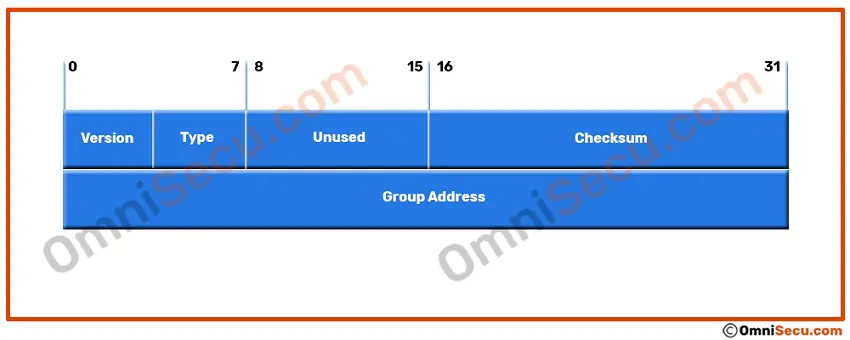
IGMPv1 message consists of 64 bits (8 octets). The original definition of IGMPv1 (RFC 1112) had the first 8 bits divided into two 4-bit fields. First four bits of first octet were used to represent "Version" and the next four bits were used to represent "Type". But later, these two fields were combined together into a single 8-bit "Type" space.
IGMPv1 messages are encapsulated in IPv4 header. The Protocol number for IGMP is 2.
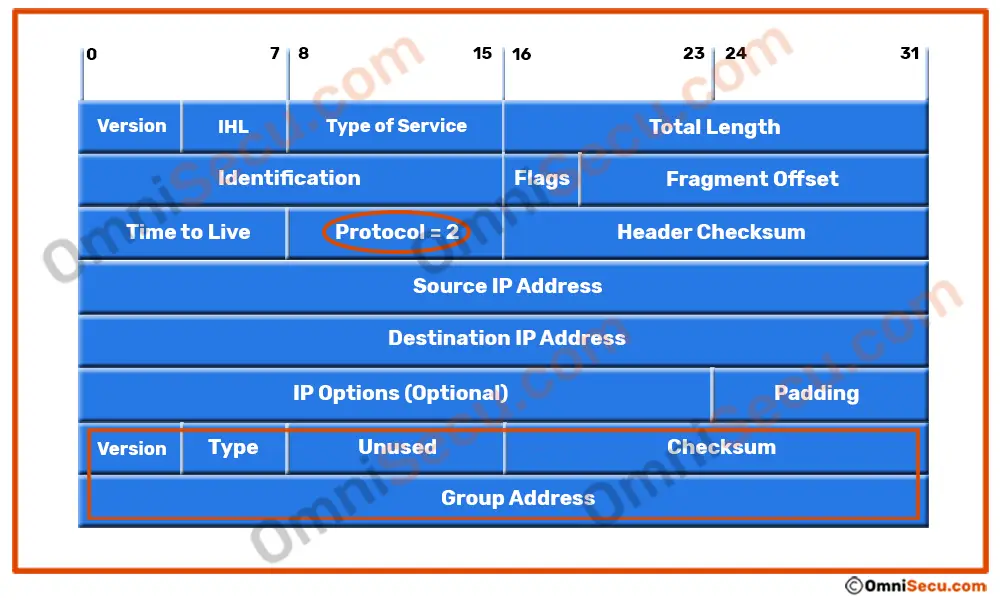
Type field of IGMPv1 message
Type field is used to identify different types of IGMP messages. Please refer following table to know different Type values in IGMPv1 message.
| Message Type | Type value number |
|---|---|
| IGMP Membership Query (MQ) messages | 0x11 |
| IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) messages | 0x12 |
Checksum field of IGMPv1 message
The Checksum field is 16-bit in length and it contains a 16-bit checksum for the message.
Group Address field of IGMPv1 message
Group Address field in IGMPv1 message contains the Class D multicast address of the group being reported.
How IGMPv1 works
IGMPv1 Join messages
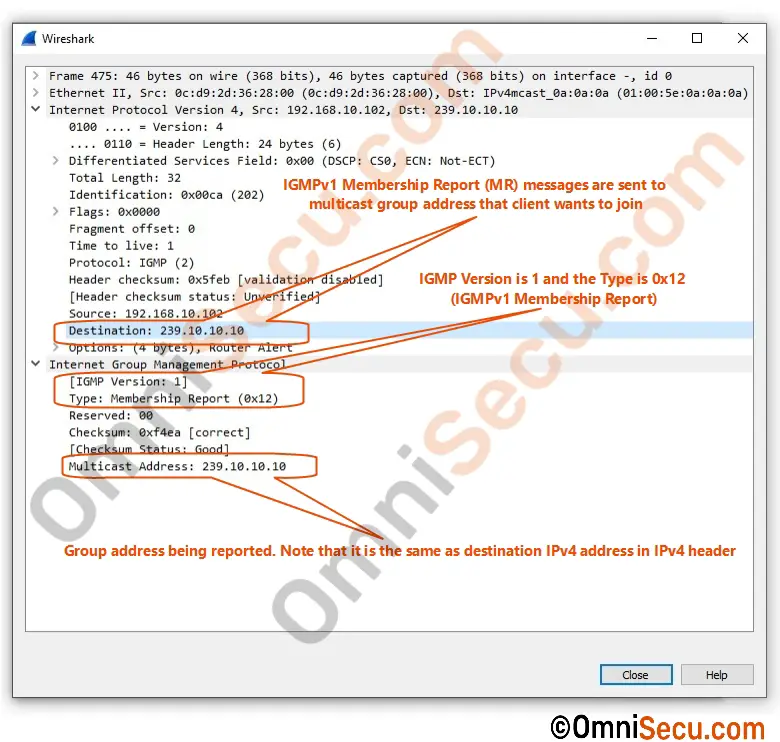
In IGMPv1, multicast clients interested in joining a multicast group generate and send unsolicited Membership Report (MR) messages. IGMPv1 Membership Report messages are sent to the multicast group address they wanted to join. Membership Report messages (MR) contains the multicast address of the multicast group they want to join. IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message Type number is 0x12.
There is no separate Type of IGMPv1 Join message. An unsolicited IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message is used as IGMPv1 Join message.
So, what is the meaning of the word "unsolicited" here? We have already discussed in the previous lesson (IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)), that IGMP has a Query-Response type of operation. Querier will send Membership Query (MQ) messages and multicast clients will respond with Membership Report (MR) messages. An unsolicited IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message is a self-initiated message sent by a multicast client not as a reply for an IGMPv1 Membership Query message.
IGMPv1 Membership Query messages are sent periodically. When a computer wants to join a multicast group, it needs to wait until the next IGMPv1 Membership Query message from the Querier (local multicast router) to prepare and send a Membership Report message to join a multicast group. An unsolicited IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message can reduce the Join latency time period also.
A computer maintains a list of multicast groups that it had joined. If a new multicast group subscription is required, the computer will send again an unsolicited IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message to join that multicast group. IGMPv1 Join messages (or unsolicited Membership Report (MR) messages) for a multicast group are sent twice, one after the other.
A Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv1 Membership Report (MR) message is copied below.
IGMPv1 Membership Query (MQ) messages
The local multicast router periodically sends out Membership Query (MQ) messages to verify that at least one multicast client is available in the subnet which is interested to receive traffic from that particular multicast group. If there is no reply to IGMPv1 Membership Query (MQ) messages from a subnet for a particular number of attempts, the local multicast router will stop forwarding the multicast traffic addressed to the particular multicast group to that subnet.
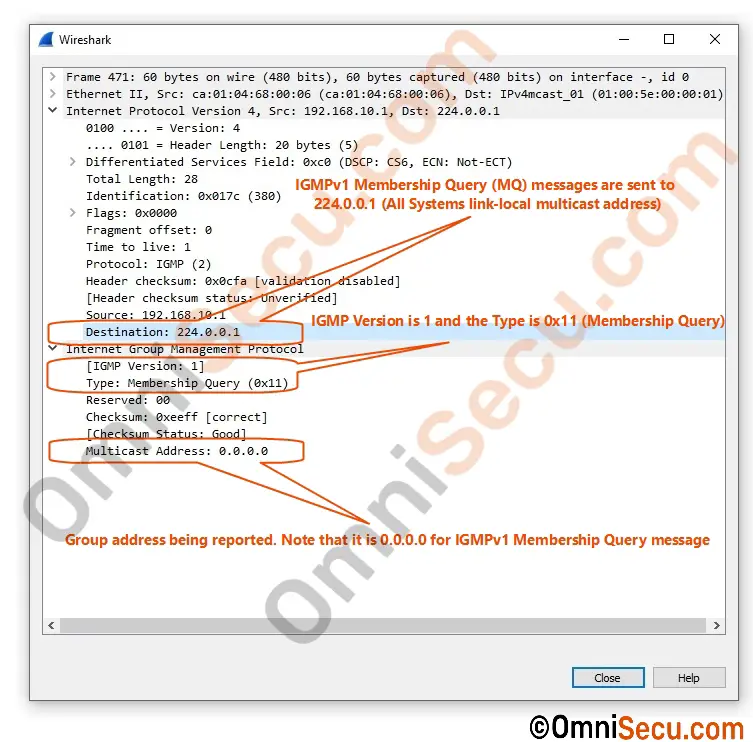
IGMPv1 Membership Query messages (MQ) are sent to All systems link-local multicast address, 224.0.0.1.
A Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv1 Membership Query (MQ) message is copied below.
IGMPv1 Leave Group process
Main point to note about IGMPv1 is that IGMPv1 does not have any Leave Group message to inform the local router about a multicast client’s intention to leave a multicast group. While using IGMPv1, if a multicast client is no longer interested in receiving multicast traffic from a particular multicast group, it does not reply to the Membership Query (MQ) messages sent from the local multicast router for that group. Since there is no Leave Group message in IGMPv1 to inform a local multicast router instantly that a multicast client wants to leave a multicast group (stop receiving traffic from that particular multicast group), the router may stream multicast traffic to the subnet for a short period even after all multicast clients left that particular multicast group.
DR and Querier roles are performed by the same router in IGMPv1.