What is multicast
Multicast is a type of network communication which lies (in concept) between unicast (send one receive one type of network communication) and broadcast (send once receive all type of network communication) in functionality. Multicast is can be defined as "send once receive many" type of network communication. Multicast type of network communication consumes less network bandwidth utilization and conserves other system resources.
Before continuing further, I suggest you to visit and learn following lessons.
- Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
- Datalink layer of TCP/IP model
- Ethernet Frame Format
- MAC addresses
- Broadcast MAC Address - ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- IPv4 multicast MAC Addresses
- Network layer of TCP/IP model
- IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
- IPv4 addresses
- Class D multicast IP addresses
- Multicast IPv4 address to MAC address mapping
- What is limited broadcast in IPv4 and how limited broadcast works
- What is directed broadcast in IPv4 and how directed broadcast works
- Transport layer of TCP/IP model
- TCP/IP Encapsulation and Decapsulation
- What is multicast group
- Comparison of multicast with unicast and broadcast
- Advantages and disadvantages of multicast
- How IPv4 multicast works on LAN
Multicast type of network communication is most beneficial for streaming type of traffic. Examples; Online TVs, Video conferencing, Virtual classroom applications, Stock exchange applications, Large scale Operating System deployment using software images etc. Therefore, UDP is used as layer 4 (Transport layer) protocol for multicast. TCP is not used as layer 4 (Transport layer) protocol for multicast. Please note that multicast is not an alternative for unicast (one to one type of network communication). But multicast sent to all computers is broadcast.
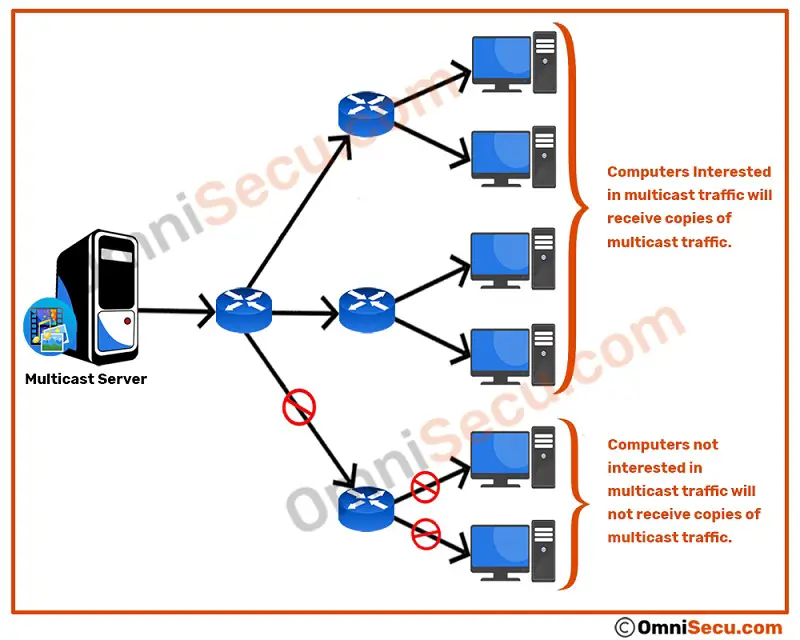
Please refer below image. A group of computers intersted in a particular stream of packet receives the IPv4 data packets belongs to that stream. Computers which are not interested in that stream is not flooded with unwanted traffic.
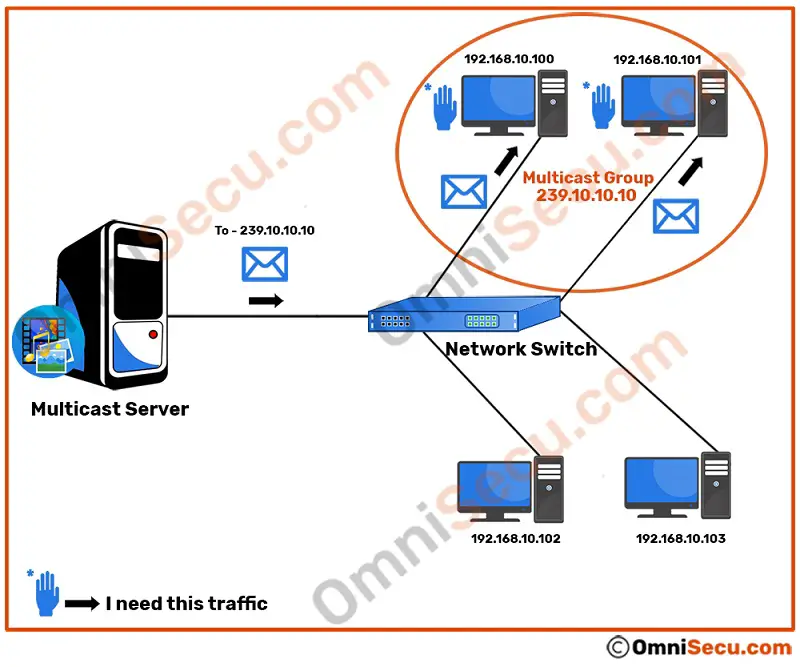
In multicast, there exists a term called multicast group. Computers those wants to receive a stream of multicast traffic, must become a member of related multicast group. Multicast group is a group of computers interested in receiving a particular data stream sent from a multicast server. A multicast server sends multicast traffic to the multicast group and all the members in that multicast group receive the multicast traffic.
Please refer below image.
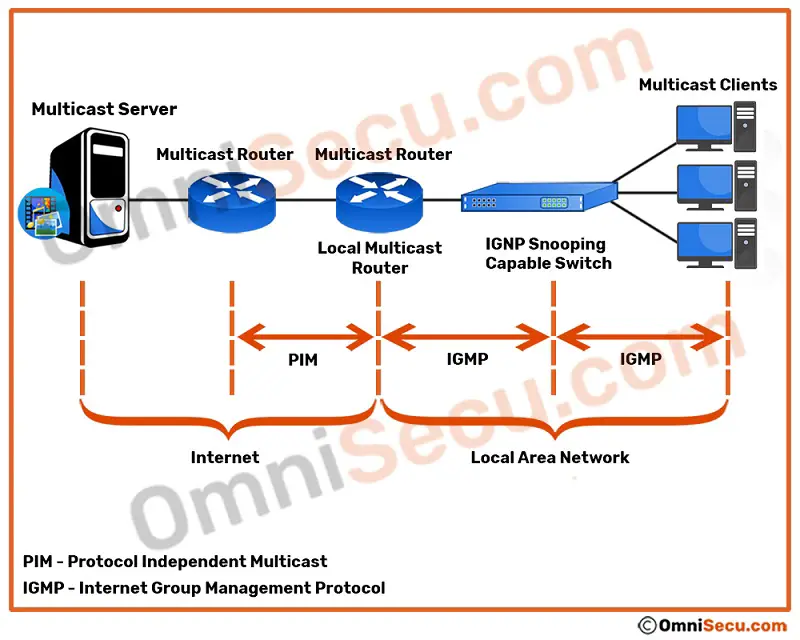
In IPV4, multicast type of network communication is built mainly using two protocols listed below.
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) - As you can see from below image, IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) operates in Local Area Network (LAN). IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) is a protocol allows a computer to advertise its multicast group membership in Local Area Network (LAN), especially to routers.
- Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) - PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast) is another multicast protocol that advertises multicast sources and receivers in a routed layer 3 network. As you can see from below image, PIM operates in Layer 3 (between routers).