IGMPv3 - Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3
The latest version (and probably the final version) of IGMP is IGMPv3. IGMPv3 is defined in RFC 3376 and then updated by RFC 4604. The main improvement IGMPv3 has, when compared with IGMPv2, is the support for Source-Specific Multicasting (SSM). Source-Specific Multicasting (SSM) allows the multicast clients to specify the unicast source address also, from where it want to receive multicast traffic. Please note that source address and group address are different. Normally represented by (S,G); where ’S’ represents the unicast source address and ’G’ represents the multicast group address. In other words, in IGMPV3 the multicast clients can specify the unicast IPv4 source address of the stream also.
Please visit below links and learn the concepts of IPv4 multicast before proceeding further.
- Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
- Broadcast domain
- Broadcast MAC Address - ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- IPv4 multicast MAC Addresses
- IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
- IPv4 addresses
- Class D multicast IP addresses
- IPv4 link-local multicast addresses
- IPv4 Internetwork control block multicast addresses
- IPv4 Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) address reservation
- IPv4 GLOP multicast addresses
- Administratively scoped multicast address block or Limited scope addresses
- Multicast IPv4 address to MAC address mapping
- TCP/IP Encapsulation and Decapsulation
- What is multicast
- What is multicast group
- Advantages and disadvantages of multicast
- Comparison of multicast with unicast and broadcast
- Advantages and disadvantages of multicast
- How IPv4 multicast works on LAN
- IGMP, What is IGMP, How IGMP works
- IGMP message types
- IGMP DR and Querier
- IGMPv1 - Internet Group Management Protocol Version 1
- IGMPv2 - Internet Group Management Protocol Version 2
- What are SSM (Source-specific Multicast) and ASM (Any-source Multicast)
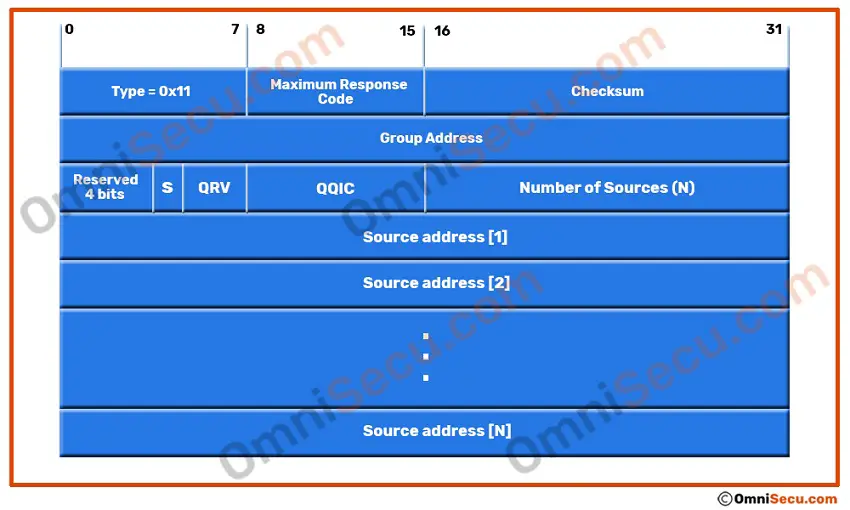
IGMPv3 Membership Query (MQ) message format
Below image shows the format of IGMPv3 Membership Query (MQ) message.
Type field of IGMPv3 message
Type field is used to identify different types of IGMPv3 messages. Please refer following table to know different Type values.
| Message Type | Type value number |
|---|---|
| IGMP Membership Query (MQ) messages | 0x11 |
| IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) messages | 0x22 |
The Maximum Response Time of IGMPv3 message
The Maximum Response Time field of IGMPv3 message is used in Membership Query (MQ) messages. Maximum Response Time field specifies the maximum time a host can wait before sending a Membership Report message for a corresponding Membership Query message. The Maximum Response Time field is for Membership Query type of messages. In other type of IGMPv3 messages, it is set to 0. The Maximum Response Time field has its unit in 0.1 second (1/10th of a second).
Checksum field of IGMPv3 message
The Checksum field is 16-bit in length and it contains a 16-bit checksum for the message.
Group Address field of IGMPv3 message
Group Address field in IGMPv3 message contains the Class D multicast address of the multicast group.
S Flag
S Flag is used to suppress processing by routers. This field indicates that the routers that receive this message should not process it.
QRV (Querier Robustness Variable Value)
The QRV (Querier Robustness Variable) field carries a parameter that is used in tuning timer values for packet loss. QRV (Querier Robustness Variable) value causes all hosts to adjust their Robustness Values which in turn affect various timers and retry counts. Increasing QRV (Querier Robustness Variable) provides more protocol robustness at the expense of latency.
QQIC (Querier’s Query Interval Code)
The QQIC field (Querier’s Query Interval Code) contains a value specifying the query interval (in seconds) used by the originator of the query.
Number of Sources (N)
Number of sources field is used to indicate how many sources are contained within the query message (Non-zero for Group-and-Source Query).
Source Addresses
Source Addresses list is used to identify N number of IPv4 unicast source addresses. The value N corresponds to the Number of Sources field.
IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message format
Below image shows the format of IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message.
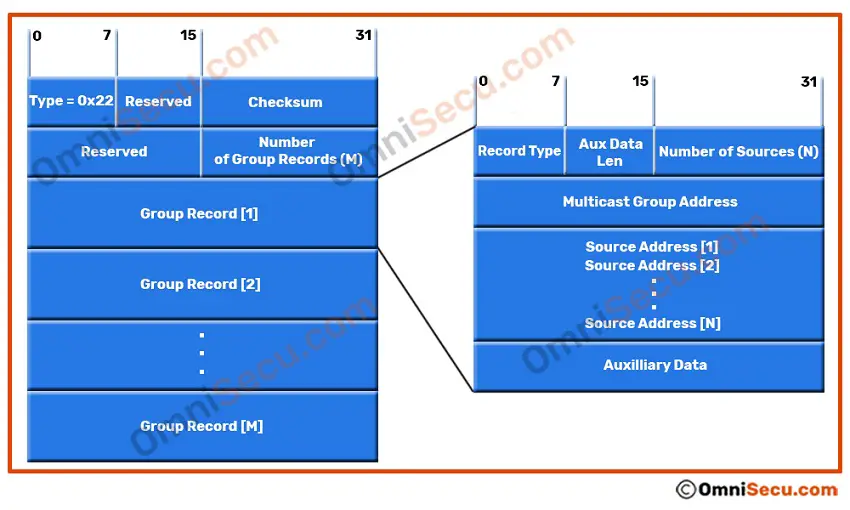
Number of Group Records
Number of Group Records field is used to indicate the number of group records. Mainly meant for Source-specific multicast (SSM), where the multicast client can specify the unicast source IPv4 address.
Record Type
There are different Types of Group Records in an IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message. Record Type is used to indicate the Type of Group Records. The Record Type field in IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message can have values Current-State Record, Filter-Mode-Change Record, or Source-List-Change Record.
- Current-State Record : Current-State Record is sent by a multicast client computer as a reply to a IGMPv3 Membership Query message sent from local multicast router asking for the current state. MODE_IS_INCLUDE is used to indicate that the multicast client wants to receive multicast traffic sent to a multicast group from the listed unicast IPv4 source addresses. MODE_IS_EXCLUDE is used to indicate that the multicast client does not want to receive multicast traffic sent to a multicast group from the listed unicast IPv4 source addresses.
- Filter-Mode-Change Record : Filter-Mode-Change Record is sent by a multicast client computer when the filter mode changes. CHANGE_TO_INCLUDE_MODE is used to indicate that the filter mode has changed from EXCLUDE to INCLUDE. CHANGE_TO_EXCLUDE_MODE is used to indicate that the filter mode has changed from INCLUDE to EXCLUDE.
- Source-List-Change Record : Source-List-Change Record sent by a multicast client computer when the source list changes. ALLOW_NEW_SOURCES is used to indicate that unicast Source Address fields in this Group record contain additional sources. BLOCK_OLD_SOURCES is used to indicate that the Source Address fields in this Group record contain the sources from which the multicast client no longer wants to receive multicast traffic.
Please refer below table to know the possible Record Type values in IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message’s Group Record.
| Record Type | Record Type value number |
|---|---|
| MODE_IS_INCLUDE | 1 |
| MODE_IS_EXCLUDE | 2 |
| CHANGE_TO_INCLUDE_MODE | 3 |
| CHANGE_TO_EXCLUDE_MODE | 4 |
| ALLOW_NEW_SOURCES | 5 |
| BLOCK_OLD_SOURCES | 6 |
Auxiliary Data Length
The Auxiliary Data Length field contains the length of the Auxiliary Data field in this Group Record. This field is in units of 32-bit words.
Multicast Address
Multicast address field indicates the multicast group address of the joined Group.
Number of Sources
Number of Sources indicates the number of Sources in the list.
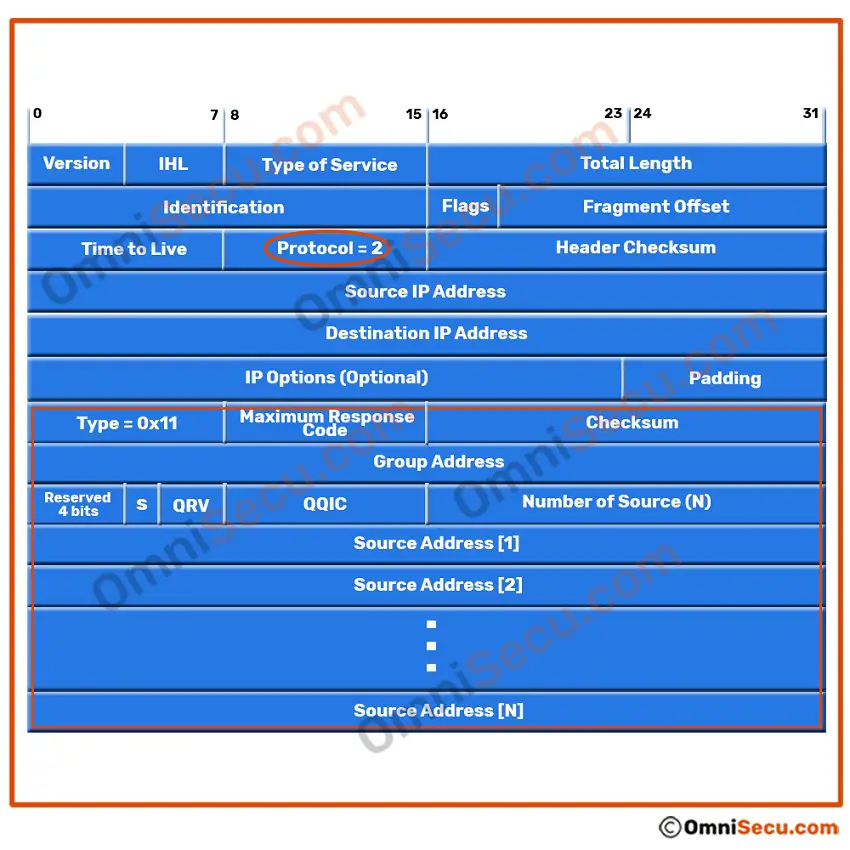
IGMPv3 messages are encapsulated in IPv4 header. The Protocol number for IGMP is 2. Following is a graphical representation of IGMPv3 Membership Query (MQ) message encapsulated in IPv4 header.
Source filtering in IGMPv3
IGMPv3 has support for SSM (Source-specific multicast) and source filtering. Previous versions of IGMP do not have support for SSM (Source-specific multicast) and source filtering. Source filtering allows a multicast client to signal to the local multicast router that from which multicast group the client wants to receive multicast traffic and also from which unicast IPv4 source address. The filtering information allows the local multicast router to forward traffic only from the sources indicated by the multicast client. Two filter modes in IGMPv3 source filtering are INCLUDE mode and EXCLUDE mode.
- INCLUDE mode : In INCLUDE mode, the multicast client signals the local multicast router that it need to receive multicast traffic from a particular multicast group, but from the listed unicast source IPv4 addresses.
- EXCLUDE mode : In EXCLUDE mode the multicast client signals the local multicast router that it need to receive multicast traffic from a particular multicast group, but not from the listed unicast source IPv4 addresses.
How IGMPv3 works
IGMPv3 Join Messages
Similar to IGMPv1 and IGMPv2, unsolicited IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message is used in join process, but remember the following points. 1) We have the concept of SSM (Source-specific multicast) and source filtering in IGMPv3. 2) As discussed above, we also have source filtering based on INCLUDE mode and EXCLUDE mode.
The join process for multicast clients in IGMPv3 is listed below.
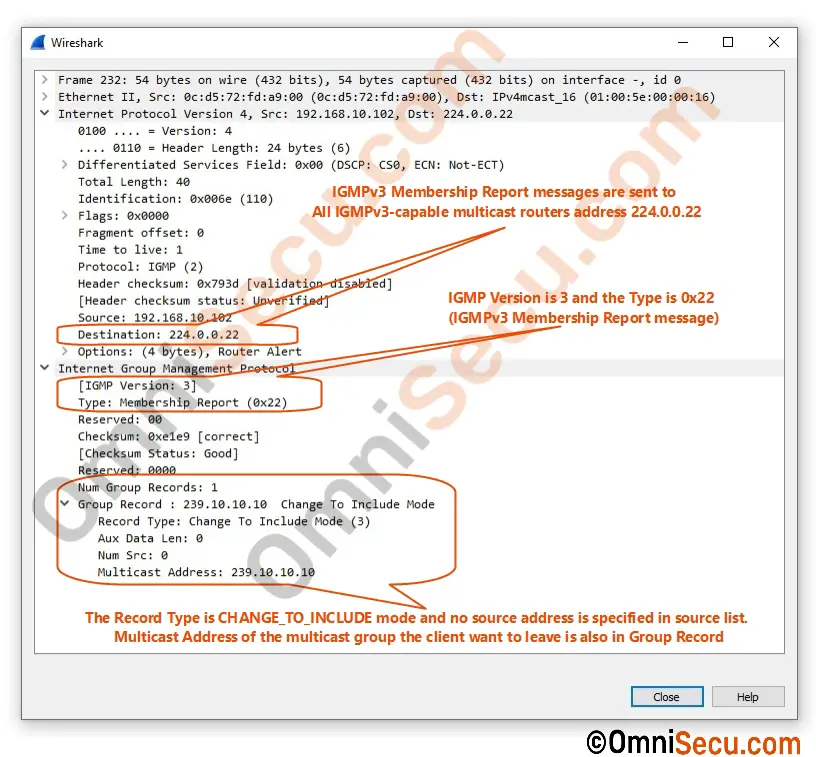
- To join a multicast group, multicast clients send IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) (twice, one after the other) to link-local multicast address 224.0.0.22 (All IGMPv3-capable multicast routers) with an empty EXCLUDE list.
- To join a specific multicast channel, multicast clients send IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) twice to link-local multicast address 224.0.0.22 (All IGMPv3-capable multicast routers) with the unicast addresses of sources included in the INCLUDE list.
- To join a specific multicast channel, excluding some unicast source addresses, multicast clients send IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) (twice, one after the other) to link-local multicast address 224.0.0.22 (All IGMPv3-capable multicast routers) with the unicast addresses of sources included in the EXCLUDE list.
A Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message sent by a multicast client for joining a multicast group is copied below.
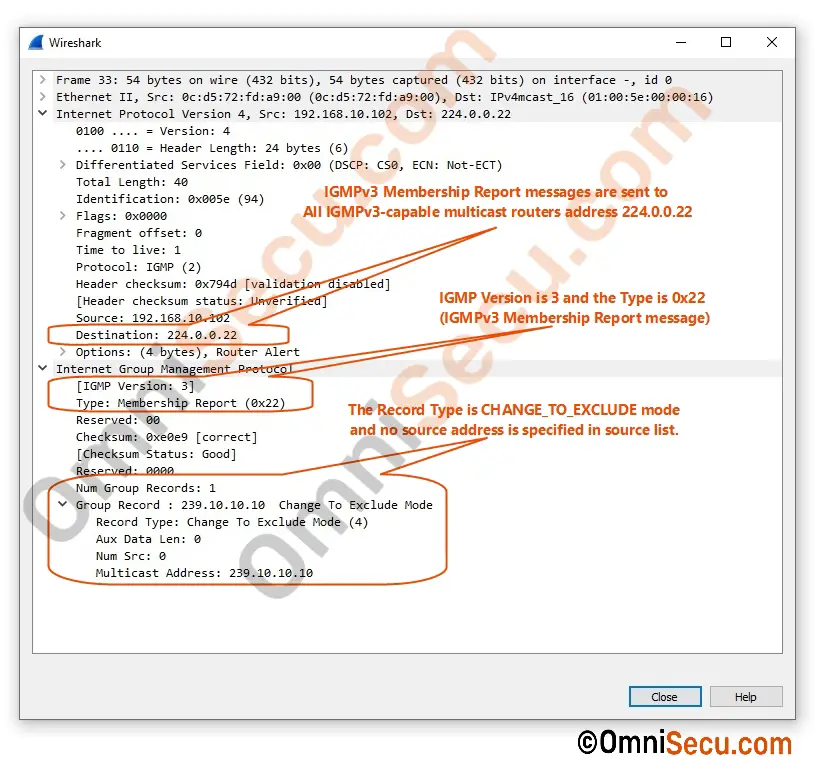
IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) Messages
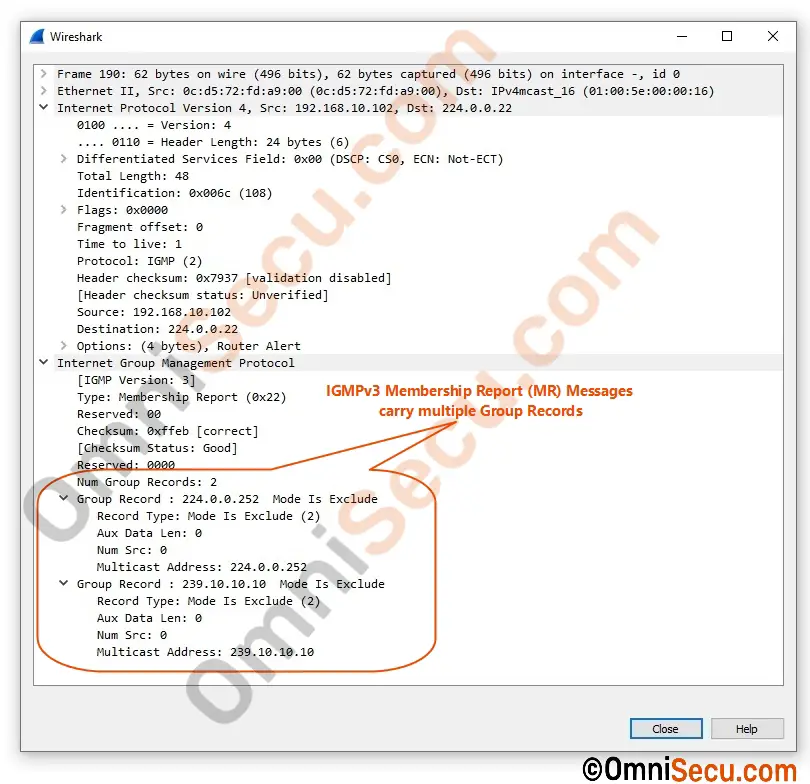
Unlike previous versions IGMPv1 and IGMPv2, IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) Messages carry multiple Group Records. Please refer IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message format above. Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message is copied below.
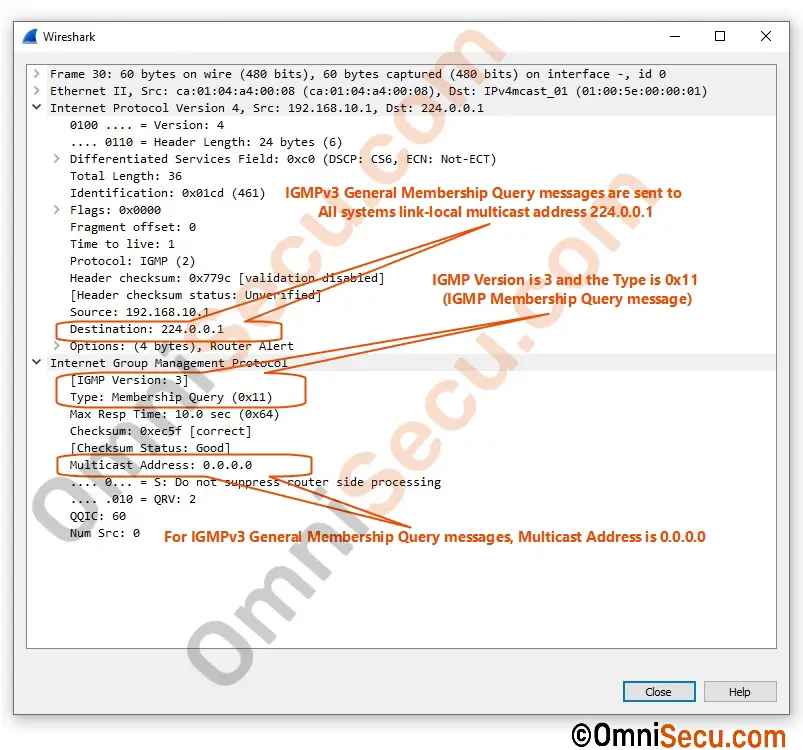
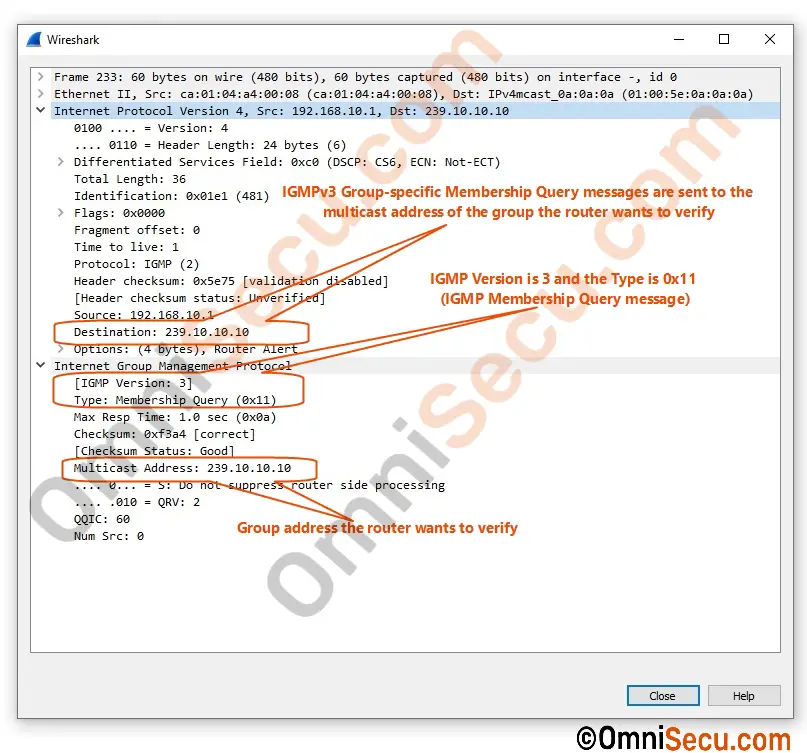
IGMPv3 Membership Query (MQ) Messages
The local multicast router periodically multicasts IGMPv3 General Membership Query (MQ) messages at All Systems link-local multicast address 224.0.0.1. All IGMPv3 based multicast clients respond by sending an IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message back to multicast router. Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv3 General Membership Query (MQ) message and IGMPv3 Group-specific Membership Query (MQ) message are copied below. Please click following link to know the difference between General Membership Query (MQ) message and Group-specific Membership Query (MQ) message.
IGMPv3 Leave Group Messages
IGMPv3 has the capability to leave from a multicast group, source, or channel using IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) messages for a multicast client. Unlike IGMPv2, there is no separate type of Leave Group message in IGMPv3. IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) messages are also used to leave a multicast group, source, or channel. IGMPv3 Membership Report (MR) message with empty INCLUDE list is used as the Leave Group message. Wireshark packet capture screenshot of IGMPv3 Leave Group message is copied below.