Names of data packets at different layers of TCP/IP model
The data packets created at different layers of TCP/IP model has different names. In this lesson, we will learn about the names of data packets created at different layers of TCP/IP model.
Following image shows five layers of TCP/IP model.
The format of the data packets generated at different layers of TCP/IP model are different, and known by different names. Please refer below image to know about the name of data packets created at different layers of TCP/IP model.
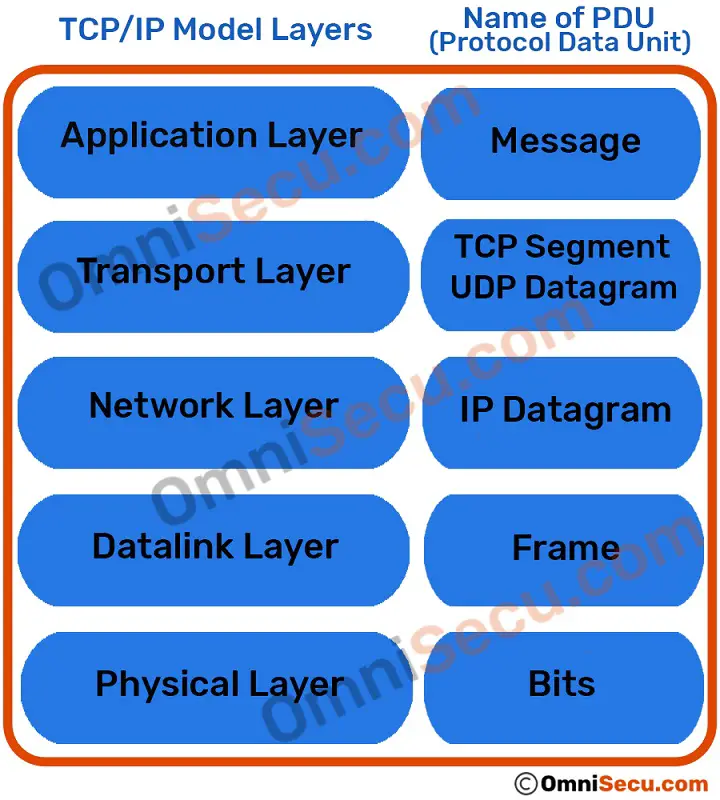
The name of data packet created at Layer 5 (Application Layer) of the TCP/IP model is "Message".
Layer 4 (Transport Layer) of TCP/IP model has two important protocols; TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol). TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) is more reliable but consumes more resource. UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is less reliable but consume fewer resources than TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is faster than TCP (Transmission Control Protocol). The Application layer message is encapsulated at the Transport layer by Transport layer protocols, TCP or UDP.
If the protocol used at the Transport Layer is TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), the data packet is known as "TCP Segment". If the protocol used at the Transport layer is UDP (User Datagram Protocol), the data packet is known as "UDP Datagram".
Main protocol at Layer 3 (Network Layer) of TCP/IP model is Internet Protocol (IP). Internet Protocol (IP) encapsulates the Transport layer data packets; TCP Segment/UDP Datagram. The data packet created at the Layer 3 (Network Layer) by Internet Protocol, is known as "IP Datagram".
Layer 2 (Datalink Layer) of TCP/IP model may further divide and encapsulates the Layer 3 IP Datagram. The data packet at Layer 2 (Datalink Layer) is known as "Frame". The Frame is finally placed on network media as bitstream for sending to destination computer at Layer 1 (Physical Layer).
To get more wider view about different layers of TCP/IP protocol stack and how they operate together, please visit and learn below lessons in order.
- Five layered TCP/IP model
- How data is moved through different layers of TCP/IP model at sending and receiving computers
- Name of data packets at different layers of TCP/IP model
- TCP/IP Encapsulation and Decapsulation
- Application Layer (Layer 5)
- Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
- Datalink Layer (Layer 2)
- Physical Layer (Layer 1)