APIPA Addresses (Automatic Private IP Addresses)
APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) is a Microsoft term used for link-local addresses. APIPA addresses are link-local IPv4 addresses which are used for network communications only within the network segment (broadcast domain). Usually link-local IP addresses assigned automatically by stateless address autoconfiguration. Routers will never forward IPv4 datagrams packets with an APIPA address as the source IPv4 address to another network segment.
APIPA addresses are assigned by the TCP/IP protocol stack running on the Windows Operating System when no other IP addressing mechanism can be found. Thus, APIPA IP addresses allows a Windows based computer to obtain an IPv4 address automatically and communicate with other computers on the local network segment.
Normally a network adapter is assigned an IPv4 address statically (manual configuration) or dynamically by using a DHCP server. If the adapter is assigned an IPv4 address manually, then no problem arise related with a missing IPv4 address. But when a network adapter is configured to get an IPv4 address dynamically with the help of a DHCP server, and if the DHCP sever is missing in the network segment (broadcast domain), the adapter may not get an IPv4 address configured on its network adapter.
Please click following link to learn how DHCP works.
When APIPA Addresses are auto-configured to a network adapter
When a computer configured to obtain IPv4 address from a DHCP server boots up, it does not have its TCP/IP settings. A DHCP client must obtain TCP/IP settings dynamically from a DHCP server.
The DHCP client now broadcasts DHCPDiscover message as limited broadcast message to find a DHCP server in the network segment (broadcast domain) to obtain TCP/IP settings from the DHCP server.
In normal situation, after receiving the DHCPDiscover message, a DHCP server will respond back with a DHCPOffer message to DHCP client. But consider that the DHCP server in the network segment is down.
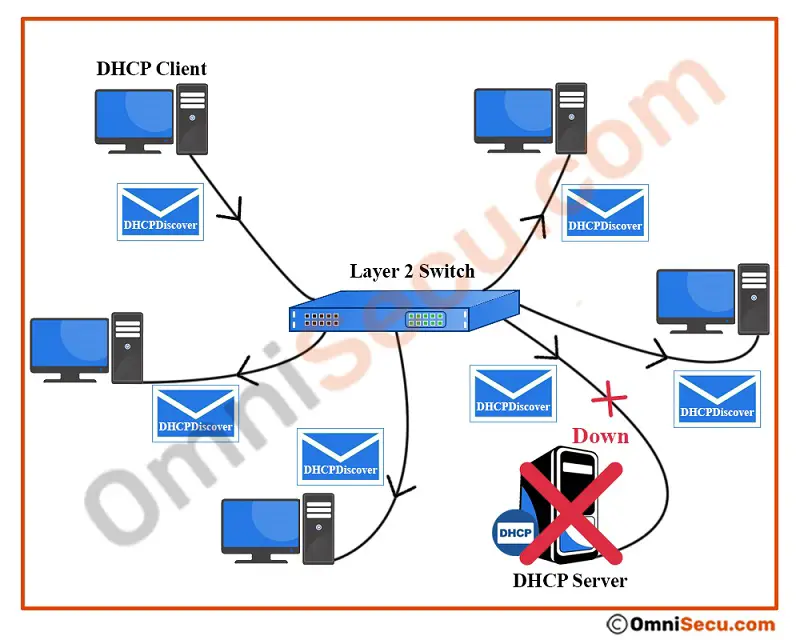
If there is no DHCP server in the network segment (broadcast domain), or the DHCP server is not working properly, the computer will not get the DHCPOffer message. The computer still continues to send DHCPDiscover message in search of a DHCP server to get an IPv4 address and other related TCP/IP settings.
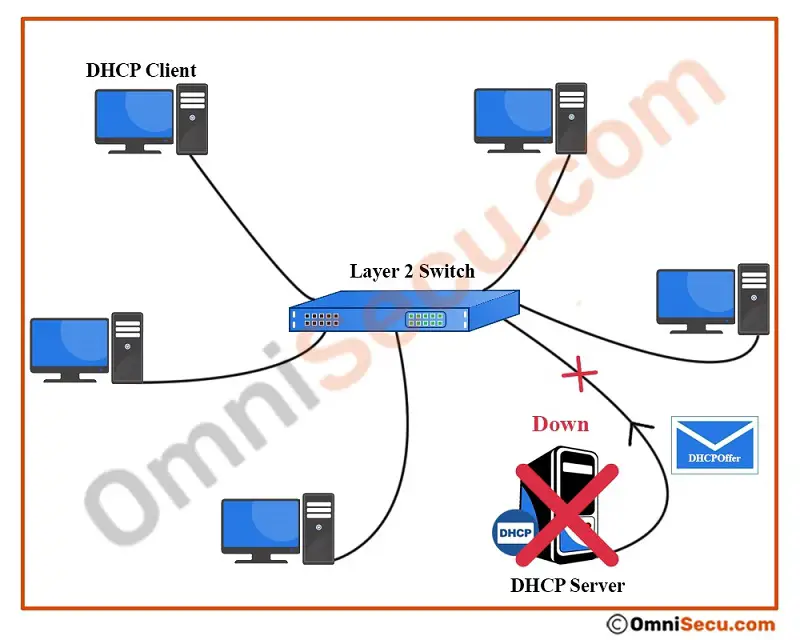
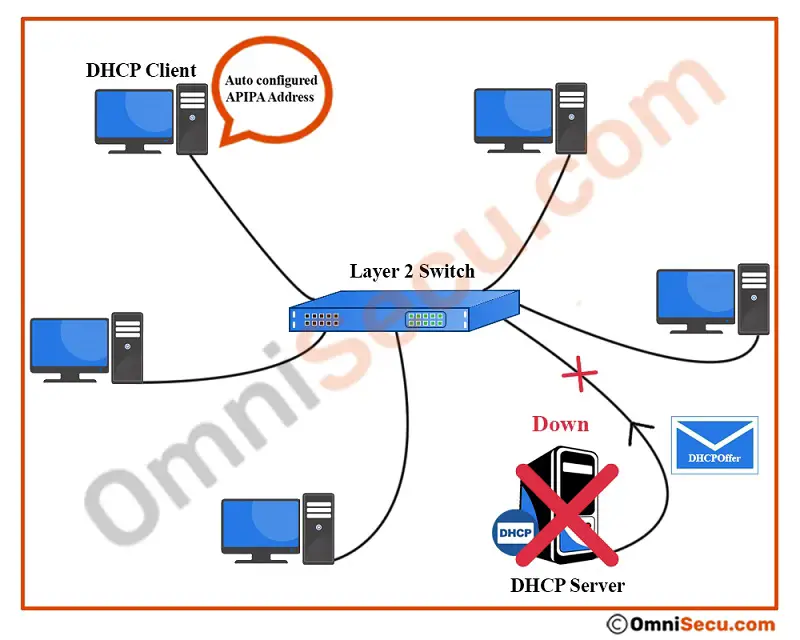
If the computer failed to get a DHCPOffer message from a DHCP server after sending many DHCPDiscover messages (a pre-configured number), the computer will auto-configure an APIPA address itself to the network adapter. APIPA address is a Class B IPv4 address in the range of 169.254.0.1 to 169.254.255.254. The subnet mask used is Class B default subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.
Please note that before assigning an APIPA address, an IP address conflict check is also performed.
How to configure a Windows machine to obtain APIPA Addresses (Automatic Private IP Addresses) in a Windows machine.
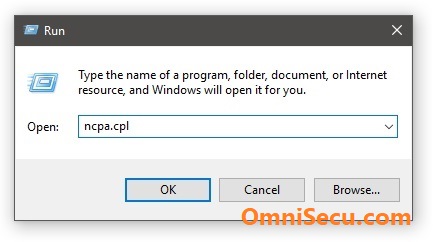
1 - Open run dialog box and type ncpa.cpl as shown in below image and click "OK" to open Network Connections.
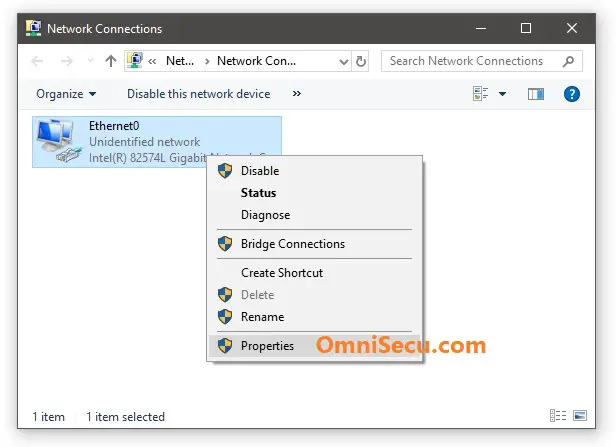
2 - Right click the network adapter and click "Properties".
3 - Select TCP/IPv4 and then click "Properties".
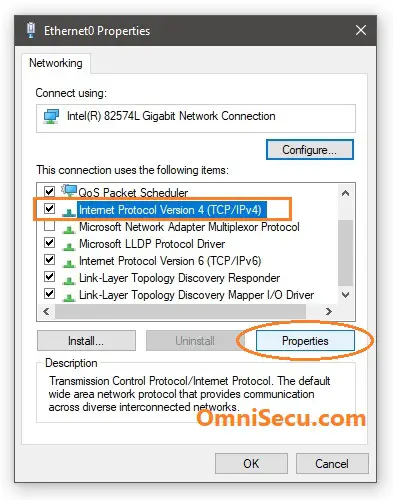
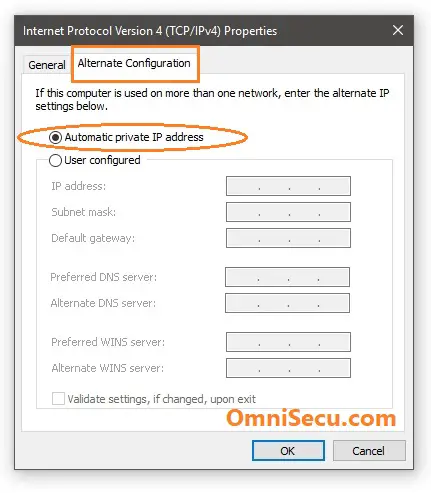
4 - Select "Alternate Configuration" tab as shown below. Here you can select APIPA address or other user configured IPv4 address and other TCP/IP settings, when dynamic addresses are not available.