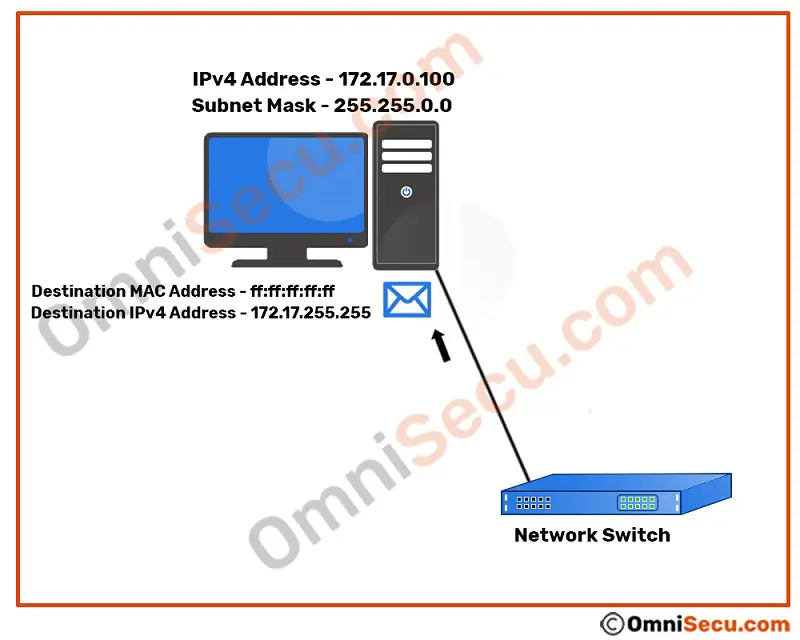
What is directed broadcast in IPv4 and how directed broadcast works
Directed broadcast is another type of IPv4 broadcast. In IPv4 directed broadcast, the IPv4 packet for broadcast is sent as unicast from one network and later that packet become broadcast in another network.
We have learned about limited broadcast in previous lesson. In limited broadcast, the router of the Local Area Network (LAN) does not forward the broadcasted packet to any of its other connected network segments. Thus, the broadcast is limited within the Local Area Network (LAN) or the broadcast domain. But in directed broadcast, the broadcast is sent from one network to another network as unicast IPv4 datagram packet. When the directed broadcast packet sent as unicast from one network reaches the destination network, it will be broadcasted at the destination network.
Before continuing further, I strongly suggest you to visit and learn following lessons.
- Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
- Broadcast domain
- Benefits of segmenting a network using a Router
- Datalink layer of TCP/IP model
- Ethernet Frame Format
- MAC addresses
- Broadcast MAC Address - ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
- Network layer of TCP/IP model
- IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
- IPv4 addresses
- IPv4 Limited broadcast address
- IPv4 Directed broadcast address
- What is directed broadcast in IPv4 and how directed broadcast works
To understand the concept of directed broadcast, refer below image.
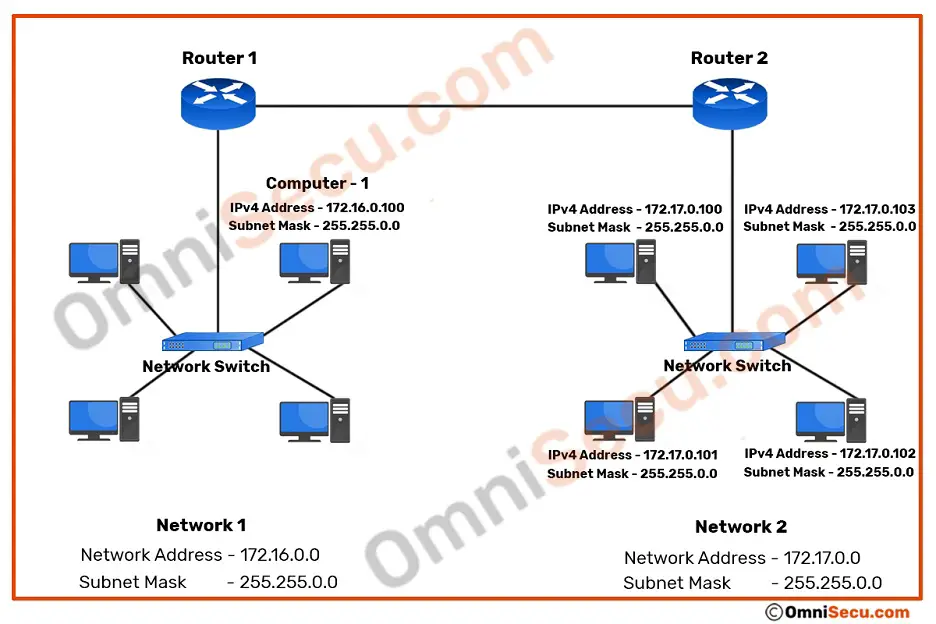
Consider Computer-1 with IPv4 address 172.16.0.100 want to send a broadcast to 172.17.0.0 network. Limited broadcast will not work here, because Router-1 will not forward the limited broadcast to another network segment. Directed broadcast is used in similar situation. IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packets are sent over the network to its destination Local Area Network (LAN) in the same way as the unicast IPv4 packets, until IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packets reach the destination netwok. Destination network’s router then encapsulates the directed broadcast IPv4 packet inside Ethernet frames with destination MAC address as broadcast MAC address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff and then forward to its Local Area Network (LAN).
Following images explain how directed broadcast works. Consider the situation where a computer with IPv4 address 172.16.0.100 wants to send an IPv4 directed broadcast to 172.17.0.0 network. Please note that 172.16.0.0 and 172.17.0.0 are different networks, separated by routers.
Computer prepares an IPv4 datagram packet with destination IPv4 address as the directed broadcast address of 172.17.0.0 network. The directed broadcast IPv4 address of 172.17.0.0 network is 172.17.255.255. Since the destination IPv4 address is not on Computer’s own network, the IPv4 directed broadcast packet will be encapsulated with Ethernet frame with the MAC address of the default gateway (router’s LAN interface). Please refer below image.
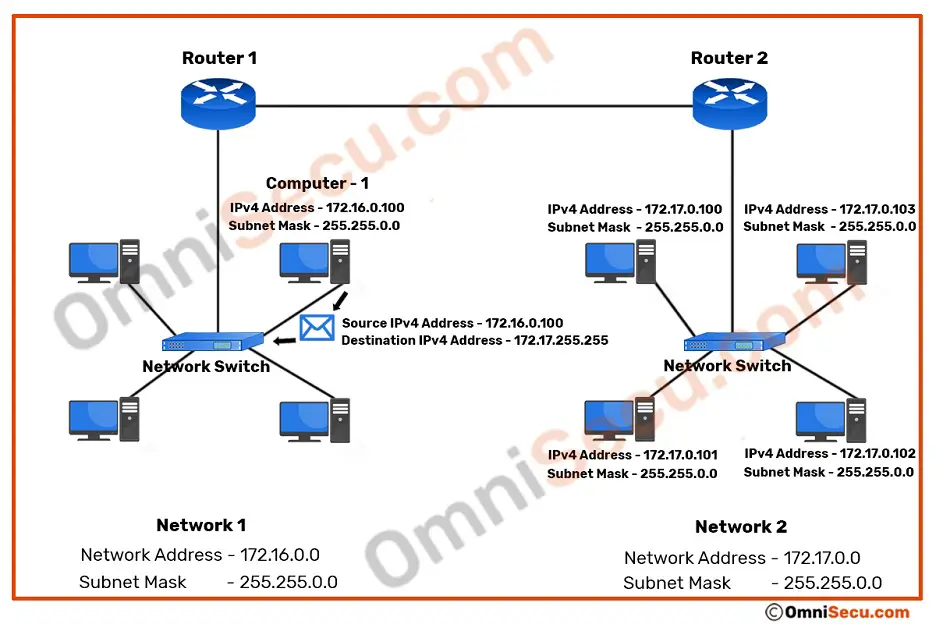
The switch will fordard the received Ethernet frame to the default gateway (router’s local interface), since the destination MAC address of the Ethernet frame is the MAC address of default gateway. Please refer below image.
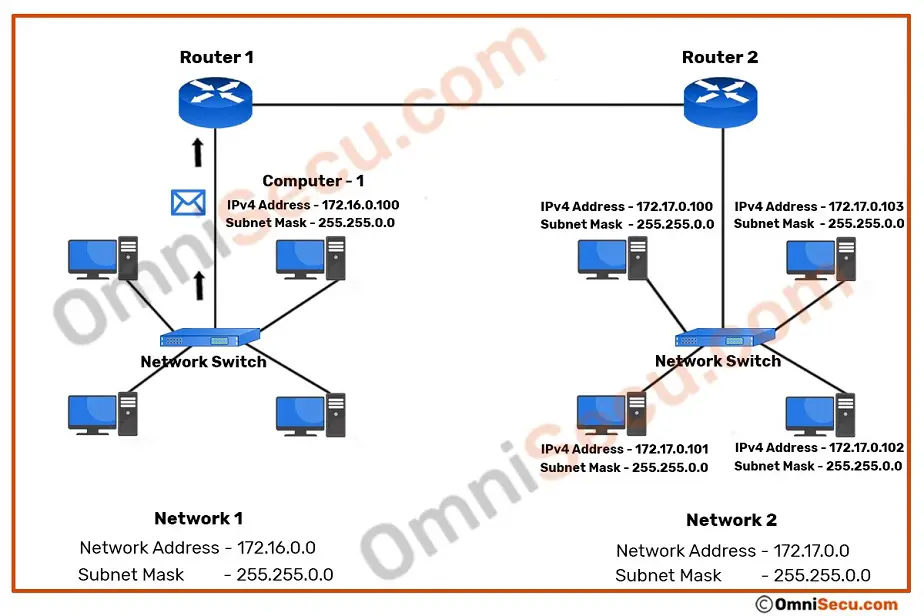
The router "Router 1" (of network 172.16.0.0), will now forward the IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packet to "Router 2" (the router of 172.17.0.0 netork) as unicast. Please refer below image.
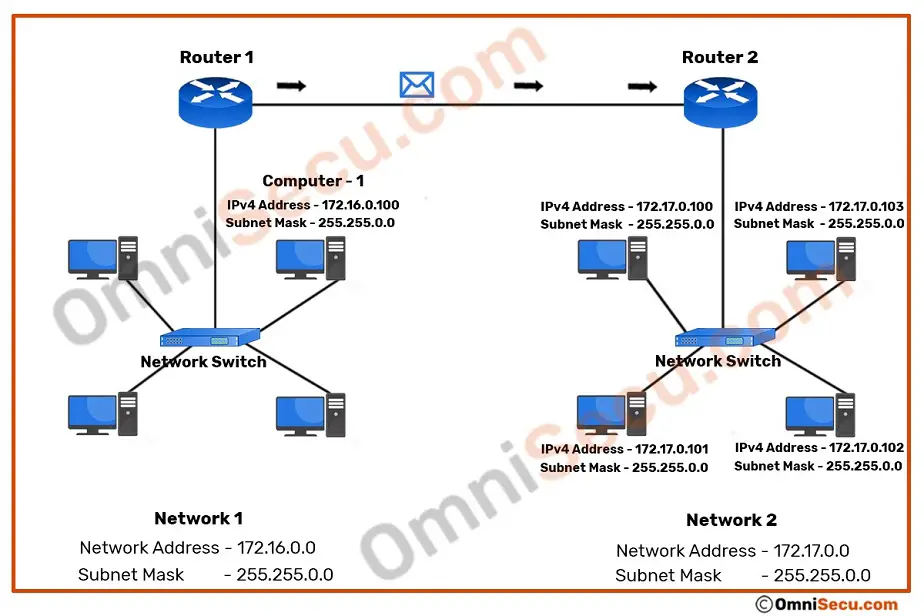
When the forwarded IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packets reaches the destination network, the router at the destination network ("Router 2") encapsulates the received IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packets with an Ethernet frame with broadcast MAC address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff as Frame’s destination MAC address. "Router 2" then forwards the encapsulated IPv4 directed broadcast datagram packet to 172.17.0.0 network. Please refer below image.
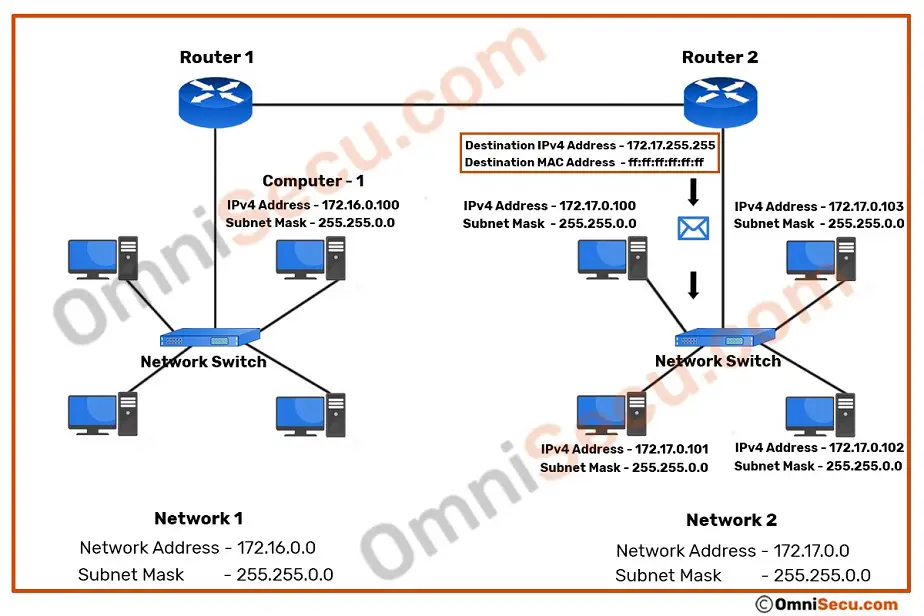
When the switch at destination network (in this case 172.17.0.0 network) finds the destination MAC address as broadcast MAC address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, switch will flood (broadcast) the packet to all its connected ports. All the connected interfaces in the destination network will receive a copy of the broadcasted packet. Please refer below image.
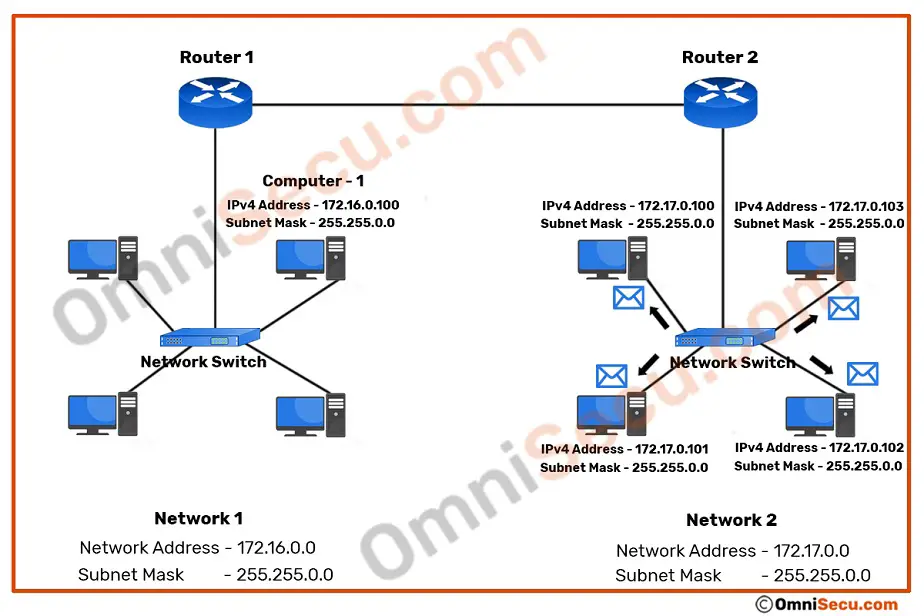
When the directed broadcast Ethernet frame is received and processed at the datalink layer of the computers inside the destination network (172.17.0.0), the datalink layer identifies the destination MAC address as broadcast MAC address ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff. Since the destination MAC address is broadcast MAC ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff, all the computers in the Local Area Network (LAN) need to accept and process the broadcasted Ethernet frame. Why? What is the reason ? Because the broadcasted Ethernet frame may contain information relevant for every device in that Local Area Network (LAN) or broadcast domain .