Class B networks and Class B IP addresses
"Class B" IPv4 addresses are used for medium-sized networks. Please note below important points about Class B network IP addresses.
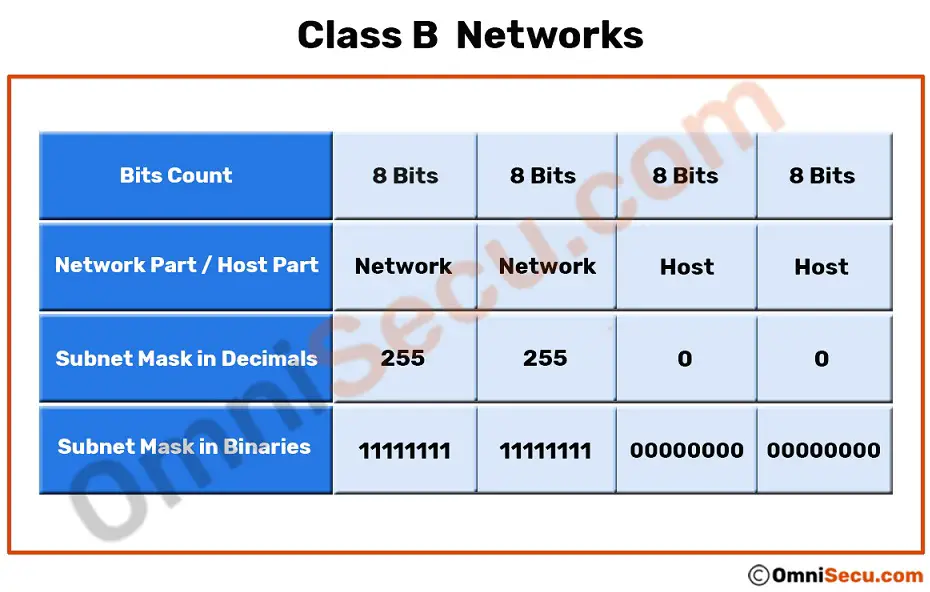
- First two octets of a "Class B" network IP address is used to identify the "Network part" and the remaining two octets are used to identify a host uniquely within that network.
- The default structure of a Class B IP address is Network.Network.Host.Host
- The left-most two bits (also called as high-order bits or most-significant bits) of the left most octet of a "Class B" network is reserved as "10".
I strongly suggest you to visit and learn below lessons before you continue learning more about Class B networks and Class B IP addresses.
- IPv4 Addresses
- What is subnet mask
- What is network address
- Binary Decimal and Hexadecimal numbers and conversions
- Five layered TCP/IP model
- Network Layer (Layer 3)
- IPv4 Protocol, IPv4 header and fields of IPv4 header
- Media Access Control (MAC) addresses
- Limited broadcast address
- Directed broadcast address
- What is Loopback address
Structure of a Class B IP address
The left-most two octets of a Class B network IP address belongs to the network part and remaining two octets belongs to the host part. The structure of a Class B IP address is Network.Network.Host.Host. The default subnet mask of a Class B IP address is 255.255.0.0.
Please refer below image.
Address range of Class B IP addresses
Since the two left-most bits (also called as high-order bits or most-significant bits) of the first octet (left-most octet) of a Class B network IPv4 address are reserved as "10", the 32 bits of a "Class B" address can be represented as 10xxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.xxxxxxxx.
The minimum possible value for the left-most octet in binaries is 10000000 (decimal equivalent is 128) and the maximum possible value for the left-most octet is 10111111 (decimal equivalent is 191). Therefore for a "Class B" IPv4 address, left-most octet must have a value between 128-191 (128.X.X.X to 191.X.X.X). Also note that the starting Class B IP address is 128.0.0.0 and last Class B IP address is 191.255.255.255.
Following image shows the range (minimum and maximum possible values) of left-most octet of a Class B network IP address. Note that two most-significant bits in left-most octet of a Class B network IP address are reserved as "10". Most-significant bits in the left-most octet are marked inside an orange rectangle in below image.
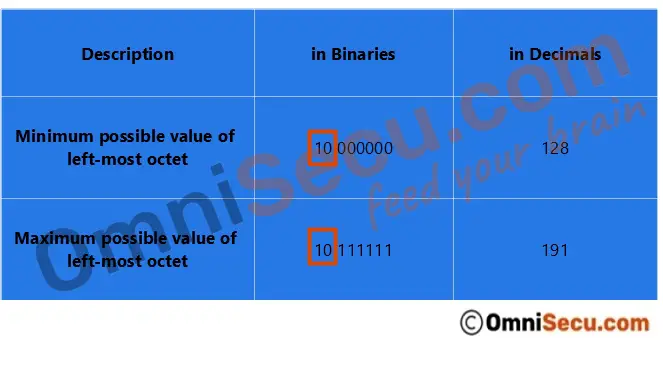
You can easily identify a Class B IP address by looking at its left-most octet. If the left most octet is between (and including) 128 and 191, it is a Class B IP address.
Since the default structure of a Class B IP address is Network.Network.Host.Host, the default subnet mask of a Class B IP address is 255.255.0.0.
Reservation of IP addresses in Class B networks
An important IP address reservation in Class B IPv4 addresses is private networks, from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255. Networks belongs to "Class B" from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.0.0 are reserved for private use and can be used inside any organization. Computers which are not connected directly to the Internet do not need globally-unique IPv4 addresses. They need an IPv4 addresses unique to that network only. Private IP addresses are used for that purpose.