ICMP Redirect messages
ICMP Redirect messages are used to make the process of routing more efficient. Consider there are two routers in a network segment. One router is the default gateway for the network segment and another router has better path to a particular destination network/host. ICMP Redirect messages are sent by a first-hop router to inform a computer inside its network segment, that there is another router in the same network segment that can deliver the packet more efficiently to that particular destination network/host.
The computers inside a Local Area Network (LAN) are configured with a default gateway to reach other networks. If a computer inside the LAN wants to send an IPv4 datagram to another network, it should sent it through the router that has the default gateway IPv4 address configured on computer’s TCP/IP settings. Consider we have two routers for an Ethernet LAN network segment. If the default gateway router knows that the second router has a better path to reach the destination network, the default gateway router will send an ICMP Redirect message to the computer. ICMP Redirect message is sent from the first-hop router (default gateway) to inform the computers in the Local Area Network (LAN) segment to use the other router which has a better path to that particular network. ICMP Redirect messages can be meant for all traffic to a particular destination network or to a specific destination IPv4 address on that particular network.
ICMP Redirect message Type number is 5. Code field values of ICMP Redirect message are explained in below table. Please click next link to know more about Type and Code fields in ICMP header
| ICMP Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Redirect IPv4 datagram for the network (or subnet) |
| 1 | Redirect IPv4 datagram for the host |
| 2 | Redirect IPv4 datagram for Type of Service and the network |
| 3 | Redirect IPv4 datagram for Type of Service and the host |
ICMP Redirect message explained with an example
There are two routers connected to the Ethernet network segment 192.168.10.0/24. Interface 192.168.10.1 of Router 1 is the default gateway for all the devices in that network segment. Network 172.16.0.0/24 is connected to an interface of Router 2. Router 1 has an entry in its routing table that the next-hop address for network 172.16.0.0/16 is 192.168.10.2.
If a computer on 192.168.10.0/24 network (in this example 192.168.10.100) wants to send a IPv4 datagram packet to 172.16.0.100, it is better to handover the packet to 192.168.10.2, not 192.168.10.1. If we handover the packet to 192.168.10.1, the IPv4 datagram packet has to traverse an additional hop.
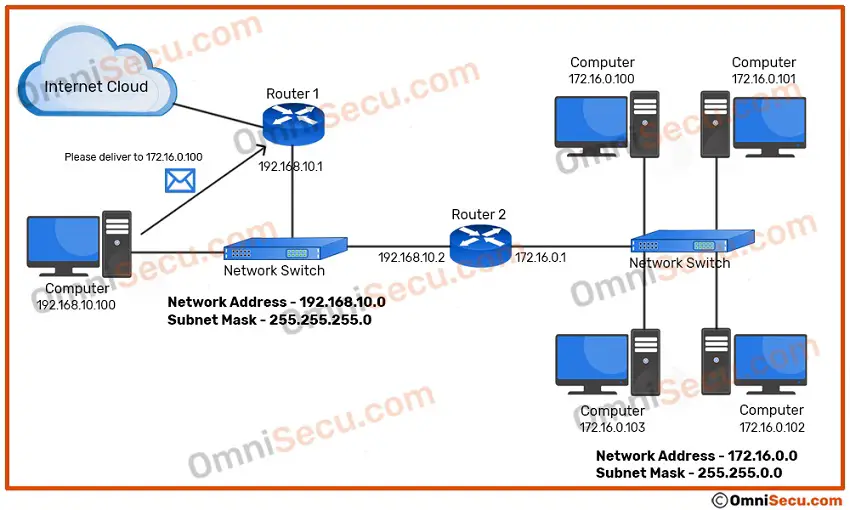
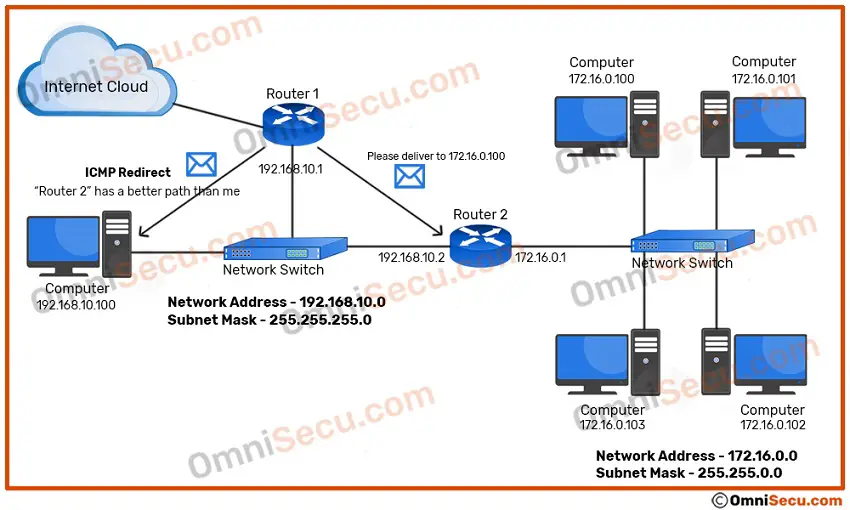
In this case, Router R1 will inform the computer 192.168.10.100 using an ICMP Redirect message that it is better to forward the packet to 192.168.10.2, and Router 1 will forward the original IPv4 datagram packet to Router 2’s interface 192.168.10.2 to deliver it to 172.16.0.100.
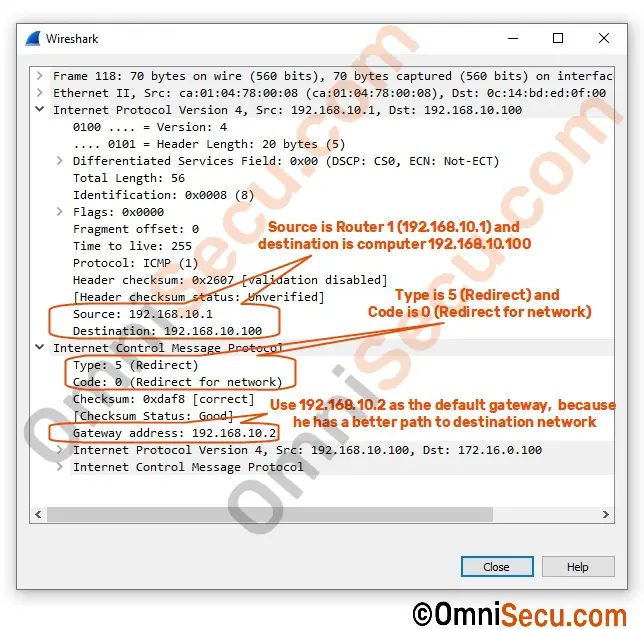
Wireshark packet capture screenshot of ICMP Redirect message (Redirect for network) is copied below.
Advantages of ICMP Redirect message
- Atleast one hop can be reduced.
- Less traffic on network links.
- Reduced router CPU load